* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 120409_Gravity LP
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
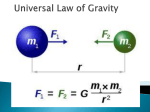
Miss Lee: 8th Grade Science (12/7/09) Gravity & Inertia AIMS / OBJECTIVES SWBAT define gravity and explain how gravity influences the motions of celestial objects. WHERE ARE WE GOING? - Current Unit: Astronomy (Unit 6) - Unit Exam will occur at completion of unit in 2 weeks CATALYST 1. List the planets in order from closest to the sun to farthest from the sun. Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune 2. Which planet do you think has the greatest gravitational pull to the sun? Which one do you think has the least? Mercury has the greatest because it is closest. Neptune has the least because it is the furthest away. MINI-LESSON/MODELING Explain Ice Skating Tickets! Show: http://www.amnh.org/rose/spaceshow/journey/ Show: http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/12760-spin-around-the-solarsystem-gravity-and-inertia-video.htm (See Below) ACTIVITY 1. The two factors that combine to keep Earth and the moon in their orbits are d. gravity and inertia 2. The tendency of a moving object to continue moving in a straight line or a stationary object to remain in place is called c. inertia 3. All objects are attracted to each other by the force of c. gravity 4. Explain how inertia and gravity combine to keep Earth in its orbit. Inertia keeps an object moving in a straight line, while gravity pulls the Earth towards the Sun. Combined, they pull the Earth in a circular orbit around the Sun. 5. Identify one factor that keeps Earth in orbit around the Sun and the moon in orbit around the Earth, both shown at right. Gravity or Inertia MATERIALS Poster, markers 6. Which of the three satellites at right (A, B, or C) would experience the greatest pull of gravity from Earth. Why? Satellite A because it is closest to Earth. 7. What holds the planets in orbit around the Sun? d. gravity 8. What four planets would experience the greatest pull of gravity from the Sun? Why? Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars (they are closest to the sun) Too easy? Try some tenth grade questions. (Look up at the board for hints!) ***Have definitions on the board 9. Does a comet have a greater pull of gravity when it is aphelion or perihelion? Why? Perihelion – because we are closer to the Sun 10. Planet A has a greater mean (average) distance from the Sun than planet B. On the basis of this information, which other comparison must be true? b. Planet A’s revolution is longer Base your answers to questions 11 and 12 on the diagram below. The diagram shows the relative strengths of the gravitational force for planets of different masses. The size of each planet represents the planet’s relative mass. The arrow length indicates the relative amount of gravitational pull that each planet would exert on an astronaut in space. 11. What is the relationship between the mass of the planets and the relative strength of their gravitational pull? The greater the mass of the planet, the greater it’s gravitational pull. ***(Explain: F α mass of 2 objects) 12. Which three planets shown have less gravitational pull than Earth? Mercury, Mars, and Pluto HOMEWORK - Write 8 sentences about what you learned (using the words: gravity, inertia, mass, force, etc.) NYS Standard Ps1.1d Gravity is the force that keeps planets in orbit around the Sun & the Moon in orbit around the Earth. Definition Force of attraction between two bodies, proportionate to their two masses and inversely proportionate to the distance between them Definition Resistance of an object to a change in its motion (an object in motion remains in motion unless a force acts upon it) G R A V I T Y I N E R T I A So What? Sun pulls the Earth towards it So What? The Earth pulls forward in a straight line