* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Computer Network
Registered jack wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
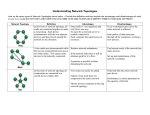
Computer Network Objectives Students will get the basic concept of Networking They will capable to identify the type of network They can select the transmission media depending upon the layout of site They will capable to select the topology depending upon the layout. They will able to understand about the different network protocols They will get the knowledge of different switching techniques. Students will know the pros and cons of peer to peer and server dedicated network They will familiar with different networking devices. Students will get the knowledge of wireless networking, Definition ****Network is a connection between two or more then two computers which are together to share resources like CD-ROM, Printer etc., to exchange files and to communicate with each others. Computer can be connected using cables, microwave, satellite and infrared rays etc. Type of Network LAN (Local Area Network) MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) WAN (Wide Area Network) LAN: This network is within a very limited area like an office building, a school, or a home. It is simpler and cheaper than other network. In a typical LAN there is a server which consist additional software and hardware. A LAN is useful for sharing resources like files, printers, games or other applications. Most local area networks are built with relatively inexpensive hardware such as Ethernet cables, network adapters, and hubs. Wireless LAN and other more advanced LAN hardware options also exist. Specialized operating system software may be used to configure a local area network. For example, Microsoft Windows provide a software package called Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) that supports controlled access to LAN resources. File Server Node 1 Node 2 Printer Node 3 Node 4 MAN: - Metropolitan Area Network extended up to a city or a larger geographical area. Through the MAN network different network can be connected. In this network mostly Brides, repeaters, routers are used to connect the computers. City Network WAN: - It is the network that is extended to a large geographical area like one country to another country. WANs often connect multiple smaller networks, such as local area networks (LANs) or metropolitan area networks (MANs). Communication is done through the satellite. It also uses routers/gateways. Source: http://www.tele-strategy.com/clientlogo/479a3979d66a4wide_area_network.gif WANs generally utilize different and much more expensive networking equipment than do LANs. Key technologies often found in WANs include SONET, Frame Relay, and ATM. The Difference between LAN and WAN LAN 1.0-2 KM 2.0-200 computer can be connected. 3.1-1000 mbps 4.Simple routing 5.Bridge/ repeaters/ hub 6.1-100 ms delays 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. WAN 100 Km or more 500 or more computer can be connected. 1-1000 mbps Complex Gateway/ router 100-ms-100s delays Advantage of Network a) Speed b) Cost c) Security d) Centralized software Management e) Resources sharing f) Communication g) Flexible Access h) Work group computing Disadvantage of Network a) Expensive to install b) Requires administrative time c) File server may fail d) Cables may brake Transmission Media The transmission of different data signals between two or more than two computer from one location to another location to share different resources is termed as transmission media. Transmission Media Wireless Media Micro Wave Satellite Mire Media Twisted pair Coaxial Cable Fiber Optic Transponder ……………………. The types of Cabling UTP 1. Twisted Pair STP 2. Coaxial Cable 3. Fiber Optic 1) Twisted Pair Twisted pair cable has fore pair of twisted cables. The Features of twisted Cables Each pair is twisted with each other to eliminate interference. Tighter the twisting, grater the transmission rate. There are five categories of twisted pair specifies by EIA/TIA Category 1: Voice only Category 1: Data up to 4 mbps Category 1: Data up to 10 mbps Category 1: Data up to 20 mbps Category 1: Data up to 100 mbps In that category 3 & 4 are widely used. The twisted pair cable is connected with the help of RJ-45 connector. The Difference between UTP & STP UTP - Outer layer is thin. - Can interference by outer data signals. - Can not carry the data signal for long distance. - It is not widely used as STP 2) Coaxial cable (coax) STP - Outer layer is thick. - Can not interference by outer data signals. - Can carry the data signal for long distance. - It is more reliable than UTP so widely used. - It is highly resist interference. - It supports greater cable length. Thin coax: 10 base2 (10 mbps up to 200m) Types Thick coax: 10 bases5 (10 mbps up to 500m) (Extras protective layer to keep moisture away from the centre conductor) Disadvantages of Coaxial Cable Difficult to install It doesn’t bend Connector: BNC connector. 3) Optical Fiber Optical fibers cabling consists a center a glass core which is surrounded by several layers of protective materials optical fiber cable transmits light signals rather than electronic signals such that electronic interference is highly eliminated. Fig: - Optical Fiber Fiber optical cable has the ability to transmit signals over much longer distance than coaxial and twisted pair cable this cable has the capability to carry information at greater speeds the cables used for services like video conference and interactive services the cost of the fiber optical is higher than others cable is difficult to install and modify. This cable is connected with the help of S-T connector. Networking Topologies The pattern of inter connection of computers in a network is called topology. According with dictionary “configuration formed by connections” is called topology. The types of Networking Topologies Bus topology or linear topology Star topology Ring topology Tree topology Mesh topology 1) Bus Topology A bus topology connects each computer to a segment called trunk. - Coaxial cables are mostly used. Terminator absorbs the signals, so it doesn’t reflect back across the bus. Signals are broadcast to all stations. CSMA/CD (carries sense multiple across / collision detection) access method is used. Advantage of bus topology Easy to implement & extend. Well suited for temporary n/w. Typically the cheapest toplogy to implement. Failure of one station (node) doesn’t affect other. Disadvantages of Bus Topology Difficult to diagnosis the error. Limited cable length & number of nods. A cable break can disable the entire n/w. Maintenance costs may be higher. 2) Star topology - All stations or nods are connected to the central hub - Adding & removing computers is easy task - Twisted pair cable is commonly used Advantage of star topology Easy to add new stations Easy to monitor & troubleshoot Can accommodate different wiring Disadvantage of star topology Failure of hub disturbs all stations More cable required 3) Ring Topology 1 4 0000000 0000000 000 3 2 - Stations are connected serially. - No terminated ends of cables. - MAU (Multi station Access Unit) is used as control device. - Token is used to transmit data. - Twisted pair or optical fiber is used as a cable. Advantage of Ring Topology Growth of system has minimal impact on performance. All stations have equal access. Disadvantage of Ring Topology Expensive Failure of a computer affects others. Complex. 4) Tree Topology - Combination of star & bus topology. - Allow expansion of the network. Advantages of Tree Topology Point to point wiring for individual segment. Supported by several network & s/w. Disadvantages of Tree Topology It the backbone is break, the entine segement goes down More difficult to configures. 5) Mesh Topology Each computer is connected to all other computers such that more cable is required. Advantages of Mesh Topology Direct Connection between any two computers. Data transmission is fast This network more reliable. Disadvantages Mesh Topology More Cables are required. Wiring is complex. Expensive Protocol The protocol is the set of rules that govern the communication between devices in a network . The set of rules include. Access method, Topology, Cables and speed. These are different types of protocol which includes. They are highlighted below: Ethernet Local Palk Token Ring FDDI ATM Ethernet Access method=CSMALCD Topologies: Bus, star, ring Cables: Twisted Pair, Coaxial, Fiber optic Speed: 10 Mbps (Megabit per second) Local Palk Access method: CSMA/CD Topologies: Bus, star, ring Cables: Twisted Pair Speed: 230 kbps Token Ring Access method: Token passing Topologies: Ring Speed: 4 Mbps to 16 Mbps FODI (Fiber Distributed Data Interference) Access method: Token Passing Topologies: Ring Cables: optical Fiber Speed: 100 Mbps ATM (asynchronous Transfer Mode) Access method: CSMA/ CD Topologies: Ring Cables: Optical Fiber / twisted Pair Speed: 155 Mbps $ higher OSI / ISO Model [ Open system inter connection (OSI) protocol is developed by international standard organization (ISO) .this protocol describe flow of data on a computer network. In OSI model defines a “layered” architecture in the term of a protocol stack. These are specific discrete functions that take place at each layers of the protocol stake with lower layer communicate on the network; information is sent down through the protocol stack of one system; over the cable layer on the other system. OSI model consists seven layers, which are follows : (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Physical layers Data link layers Network layers Transport layers Session layers Present anion layers Application layers (a) Physical layers Establishes the physical characteristic of the network c types of cable, connectors length) Also defines electricity characteristic of signals to transmit data. The physical layers transmit binary data as electricity or optical signal. (b) Data link layers Converts frames in to bits in send side and bits in to frame in to receive side . Performs error checking. Resends acknowledgement (NIC card) (c) Network layers Concerned with addressing & routing. Logical address are converted to physical add Traffic control. IP / IPX (d) transport layer Responsible for flow control & ensuring messages are delivered or not. Error handling. TCP, UDP protocols are used. (e) session layer Establish / maintain / terminate a connection. Managing session means involves synchronization of user tasks & dialog control. Synchronization involves the use of check points in the data stream. Security function takes place at this layer. Win sock & net BIOS are used in this layer. (f) presentation layer Responsible for data translation, compression, de compression and encryption. Common protocols used in this layer are SMB, NCP and NFS. (g) Application layer User interface to network services such as file transfer / data base access. RPC is used. Switching techniques In large network, these are multiple paths to connect sinter & receive. Switching techniques are used to switch data to the receives selecting path (s). The most common switching techniques are: (1) circuit switching (2) packet switching 1. Circuit switching Circuit switching is a techniques that directly connect the sender & the receives in the broken path. In these switching techniques, once connection is established. A dedicated path exists between both ends until the connection is terminated. Advantages of circuit switching The communication channel (once established) is detailed. Disadvantages of circuit switching Possible long wait to establish a connection. More expensive then other switching techniques. Inefficient use of communication channel. 2. Packet switching In packet switching a manage is broken in to small parts called packets. Each packet is tagged with appropriate source and destination address. In these techniques, packet can be stored in main memory instead of disk; therefore access delay & cost are minimized. Transmission nodes are also optimized. Advantage of packet switching Packet switching is cost effective because switching devices don’t need massive amount of secondary storage. Packet switching offers improved delay characteristics. Packets can be retransmitted if these are any problem. Packet switching maximizes the link efficiency. Disadvantage of pocket switching Protocol for packet switching is complex. Initial high cost for implementation. Packet is lost; sender needs to retransmit the data. No dedicated path. Net work architecture 1. Clinet Servers Model 2. Peer to peer Model 1) Client serves model of networking Client Request Server Response Request Client Process Operating System Server Process Response Communicatio n Facilities Advantage of client server a. Flexibility b.Extensibility c. Modularity d.Simplicity Disadvantage a. Server may fail b.Server is a potential bullet neck c. Expensive Operating System Communicatio n Facilities 2) Peer to peer model of networking File Client Program File Server Program Server or Client A File Client Program File Server Program File Client Program B File Client Program File Server Program File Client Program Z In peer to peer model, each computer is treated as client as well as server. This model is in expensive and simple to set up and manage but main slip side (draw back) of this network is that it has limited extensibility. Network Devices Switch Repeater Bridge Router NIC (Network Interface Card) Switch It is the central connecting device, in which work station server and other device are connected Switch amplify the obtained signals Switch memorize, the all computers connected to it Often used witch star & ring topology Also called hubs. Bridge Bridge connected smaller network to form large network to form large network The bridge manages the traffic to the maintain performance Repeater It amplifies the obtained signals Repeater spark network device This device is used when total length of network exceeds standard This device is used when total length of network exceeds standard Router It delivers massage from one device to another It selects the best path to the router the message It prevents data collisions NIC (network interface card) It is like a modem but it only understand the digital signals (0 1 2 3 4 5) digital signals (0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10) analog signals It has high band width for data transmission. NIC has a drives to operate it. Exercises Objective type questions