* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Buddhism/Hinduism Presentation
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Early history of Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hindu deities wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
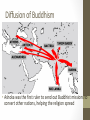
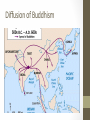
Indian Religion • Element: Explain the development and impact of Hinduism and Buddhism on India and subsequent diffusion of Buddhism. • Vocabulary: Hinduism, Brahman, atman, Dharma, Karma, Samsara, moksha, Siddhartha Gautama, Buddhism, Nirvana Development of Religion • Mahabharata: an epic Arayan tale that told of the struggle to control the southern portion of India • Krishna: one hero from the epic • Many believe that this struggle is what led the founding of Hinduism and Buddhism Hinduism Founder: • no single founder, added to over time • based on Aryan religious beliefs Homeland: • India • vast majority of Indian people are Hindus Hinduism God: Hindu’s worship many gods •Brahman = ultimate reality (God) •Hindu gods and goddesses • gave ordinary Hindus a way to express their religious feelings • three chief deities • Brahma the Creator • Vishnu the Preserver • Siva the Destroyer Hinduism Sacred Writings: • Vedas = collections of hymns and ceremonies passed down orally by Aryan priests and later written down • knowledge comes from the Vedas Hinduism: Key Beliefs • Dharma: duties you are expected to perform, the ethical way in which you are supposed to behave • Ahimsa: non-violence towards all living things Hinduism: Key Beliefs • Reincarnation • 500s B.C. • the idea that the individual soul is reborn in a different form after death • after many existences, the soul may fulfill its final goal and unite with Brahman • you may be reborn into a higher or lower caste Hinduism: Key Beliefs • Karma • an important part in reincarnation • the idea that peoples actions determine: • their form of rebirth • the class into which they are reborn, if they are reborn as a person Hinduism: Key Beliefs • caste system • religious basis created by the system of reincarnation • higher caste members worthy of privileges because of good karma • lower classes hoped to improve their social status in future lives if they behaved well in the present Hinduism: Key Beliefs • Aum (or Om) • represents Brahman, everything that is absolute in the universe \ Buddhism Description: • sixth century B.C. • new doctrine appeared in northern India • rivaled Hinduism Buddhism Founder: •Siddhartha Gautama • known as the Buddha • “Enlightened One” Buddhism Founder: • Legend: • Born into luxury, became shocked when he drove around in his chariot and saw poverty and sickness • Left wife and newborn son to wander around India at age 29 • Lived as hermit for 7 years until finally finding enlightenment Buddhism Homeland: • Northern India God: • rejects the idea of a deity Buddhism Sacred Writings: • Mahayana Sutras • The Tripitaka Ceremonies: • Buddha Day Buddhism: Key Beliefs • Four Noble Truths: 1. The truth of suffering (dukkha) • 2. The truth of the cause of suffering (samudaya) • 3. People suffer because of their material desires The truth of the end of suffering (nirhodha) • 4. All people suffer and know sadness and sorrow Suffering could end by elimination desires The truth of the path that frees us from suffering (magga) • By following the Eightfold Path one could eliminate desires Buddhism • Purpose: To reach nirvana (enlightenment) • ultimate reality • reunion with the Great World Soul • achieving wisdom is a key step • The Middle Way (eightfold path) is important • Away from extremes • Moderation 8 Fold Path Color Symbolism in Buddhism • • • • • • Blue = coolness, infinity Black = hate, primordial darkness White = knowledge, purity Red = sacred blood, life Green = balance, harmony Yellow = earth, renunciation Diffusion of Buddhism • • • • The first “great missionary faith” Spread into Afghanistan by A.D. 1 Spread into China during mid 1st century A.D. Reached Japan and Korea by A.D. 500 Diffusion of Buddhism • Ashoka was the first ruler to send out Buddhist missions to convert other nations, helping the religion spread Diffusion of Buddhism Buddhism Throughout Asia Japan Buddhism Throughout Asia China Buddhism Throughout Asia Vietnam Buddhism Throughout Asia Thailand Afghanistan Buddhism v. Hinduism • Related to Hinduism • Shares belief of: • Karma • (accumulation of good or bad deeds) • Dharma • (but in this case is the teachings of Buddha telling you how to act/live) • Reincarnation • (rebirth) • Differs: Rejection of caste system • taught that all individuals could reach nirvana as a result of their behavior in their current life Video on India • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Nn5uqE3C9w 2. Ancient Asian Civilizations • Standard: Identify the major achievements of Chinese and Indian societies from 1100 BCE to 500 CE. • Essential Question: What were the major achievements of Chinese and Indian societies from 1100 BCE to 500 CE? Assignment • Complete a Hinduism/Buddhism t-chart comparing the 2 religions. • Working in partners, students will complete the India map. • Identify the following geographical features of India: • • • • • • Hindu Kush Himalayas Khyber Pass Indus River Ganges River Brahmaputra River Summarizer • How did India’s geography impact how Buddhism and Hinduism spread?