* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Organization
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
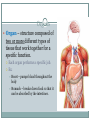
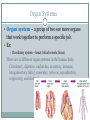
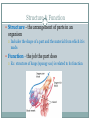
Cellular Organization FIVE LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION 7-3.1 SUMMARIZE THE LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION WITHIN THE HUMAN BODY. Levels of Organization • From smallest to largest: Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism Cells Cell – basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells make up all living things. The Benefits of Being Multicellular Larger size The larger you are, the less predators you have, and you can eat larger prey! Longer life Longer life-span than unicellular organisms. Specialization Each type of cell has a particular job. This makes the organism more efficient. Tissues Tissue – group of similar cells that perform the same function. Most animals (including humans) have four basic types of tissue: Muscle tissue Nerve tissue Connective tissue Protective tissue Muscle Tissue Muscle tissue – makes parts of your body move by contracting (shortening) and relaxing. In some cases, like throwing a ball, you control the movement. In other cases, such as the beating of your heart, the movement occurs without conscious control. Nerve Tissue Nerve tissue – carries messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of the body. Connective Tissue Connective Tissue – provides support for your body and connects all its parts. Ex: Bone – supports & protects Fat – insulation & energy storage Blood Tendons Ligaments cartilage Epithelial Tissue Functions as a boundry. Covers the surfaces of the body, inside (as lining/or covering of internal organs) and outside of the body. Organs Organ – structure composed of two or more different types of tissue that work together for a specific function. Each organ performs a specific job. Ex: Heart – pumps blood throughout the body Stomach – breaks down food so that it can be absorbed by the intestines. Organ Systems Organ system – a group of two ore more organs that work together to perform a specific job. Ex: Circulatory system – heart, blood vessels, blood There are 11 different organ systems in the human body. Circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory, immune, integumentary (skin), muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, and skeletal. Organism Organism - a living thing Structure & Function Structure - the arrangement of parts in an organism Includes the shape of a part and the material from which it is made. Function - the job the part does Ex: structure of lungs (spongy sac) is related to its function Homeostasis The different organ systems work together and depend on one another. Ex: Respiratory, digestive & circulatory systems work together to fuel muscles with the energy they need. The systems of the human body work together to maintain homeostasis. Your body is constantly regulating internal conditions. Blood sugar, posture, temperature.