* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download histotoxic clostredia
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
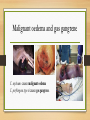
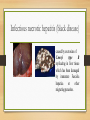
Histotoxic clostridia Bacteriology lectures By Dr. Zina Alshami Diseases caused by Histotoxic clostridia occur throw 2-typesof infection: 1- endogenous infection including: • Blackleg • infectious necrotic hepatitis • bacillary haemoglobinuria 2- The exogenous infections including: • malignant oedema • gas gangrene Blackleg C. chauvoei, Malignant oedema and gas gangrene C. septicum causes malignant oedema C. perfringens type A causes gas gangrene. Caused by C. septicum Infectious necrotic hepatitis (black disease) caused by exotoxins of C.novyi type B replicating in liver tissue which has been damaged by immature Fasciola hepatica or other migrating parasites. Bacillary haemoglobinuria • endogenous infection caused by C. haemolyticum, endospores are dormant in the liver, in Kupffer cells. Fluke migration facilitates spore germination and clostridial replication The α toxin, a phospholipase produced by vegetative cells, causes intravascular haemolysis in addition to hepatic necrosis. Extensive red cell destruction lead to Haemoglobinuria. Diagnosis 1. Fluorescent antibody techniques (FAT). 2. C. perfringens is cultured anaerobically on blood agar at 37°C for 48 hours. Colonies appear surrounded by a zone of double haemolysis. Nagler reaction produced by Clostridium perfringens growing on egg yolk agar. The Nagler reaction, a plate neutralization test, identifies the α toxin of C. perfringens, which has lecithinase activity. CAMP test • Positive CAMP test occurs with Streptococcus agalactiae A diffusible factor released by S. agalactiae enhances the partial haemolysis produced by the α toxin of C. perfringens. • PCR techniques Treatment and control • Penicillin or broad-spectrum antibiotics. • Vaccination, usually with bacterin and toxoid components in adjuvant.