* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Containing Communism
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Marshall Plan wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
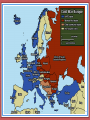
Containing Communism USII.18 American Vision Ch. 26 Sect.2 Student Objectives • Students will be able to: • Describe the policy of containment • Explain the Truman Doctrine • Explain the Marshall Plan The Long Telegram • Feb. 1946: Diplomat George Kennan wrote a telegram with his views and advice on the Soviets • Called the Long Telegram • The Soviet system was weak and could be beaten if it was kept from expanding • Policy of containment – keeping communism within its present territory through the use of diplomatic, economic, and military actions The Truman Doctrine • Speech by Truman in response to Communist aggression in Greece and Turkey became the US policy in dealing with communism • Pledged the United States to fight communism worldwide through political, military, and economic assistance to democratic nations Truman Doctrine In a dramatic speech to a joint session of Congress, President Harry S. Truman asks for U.S. assistance for Greece and Turkey to forestall communist domination of the two nations. Historians have often cited Truman’s address, which came to be known as the Truman Doctrine, as the official declaration of the Cold War. In February 1947, the British government informed the United States that it could no longer furnish the economic and military assistance it had been providing to Greece and Turkey since the end of World War II. The Truman administration believed that both nations were threatened by communism and it jumped at the chance to take a tough stance against the Soviet Union. In Greece, leftist forces had been battling the Greek royal government since the end of World War II. In Turkey, the Soviets were demanding some manner of control over the Dardanelles, territory from which Turkey was able to dominate the strategic waterway from The Marshall Plan • June 1947: Secretary of State George Marshall proposed the European Economic Recovery Program, or the Marshall Plan • The plan gave billions of dollars in supplies, machinery, and food to European nations to rebuild their economies • Opened European markets to American business and made communism less appealing • Soviet Union and its satellite nations rejected the offer, further dividing Eastern and Western Europe NATO • April 1949: the US and 11 other nations formed a mutual defense alliance called the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) • West Germany will join in 1955 • NATO members agreed to come to each other’s aid if one was attacked • In response to NATO, the Soviet Union and its satellite nations in Eastern Europe formed their own military alliance called the Warsaw Pact Class Assignment • Classwork: Close-read of the Truman Doctrine (page 1076) • Homework: Close-read of The Marshall Plan handout