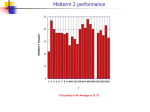
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THREE–PHASE SYSTEMS 1. A balanced Y–connected source with
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
THREE–PHASE SYSTEMS 1. A balanced Y–connected source with supplies power to a balanced Y–connected load with a per–phase impedance of . If , find the per–phase impedance of the power–distribution line. 2. The power–distribution line of a balanced Y–Y system has a per–phase impedance of . If the per–phase load impedance is and the per–phase power loss on the line is 60 W, find the per–phase power absorbed by the load as well as the per–phase complex power supplied by the source. 3. A balanced, positive–phase–sequence Y–connected source with is connected by four perfect conductor lines to an unbalanced Y–connected load having , ,y . Find the current on the neutral line. 4. If the neutral line in the Y–Y system of Problem 3 is removed, find the load neutral node referenced to that of the source neutral node. , the voltage of 5. A balanced, negative–phase–sequence Y– system has a per–phase distribution–line impedance of and a per –phase load impedance of . If , find the line currents and the phase voltages at the load. 6. A balanced Y– system has and . If the load absorbs 400W per phase with a lagging power factor of 0.875 and the distribution line absorbs 20W per phase, find , , ,y . 7. A balanced load draws a complex power of kVrms, 60Hz. at a line voltage of 4 a. Assuming a –connected load, find a simple parallel equivalent for its phase impedance. b. Assuming a Y–connected load, find a simple series equivalent for its phase impedance. 8. a. What –connected capacitor bank must be connected in parallel with the load of Problem 7 to achieve pf = 1? Assume the line voltage remains unchanged b. Repeat, but for a Y–connected bank 9. A balanced load absorbs 360kW at pf = 0.8, lagging. If the load is fed by a balanced source via a power–distribution line with a per–phase impedance of and the line voltage at the load es 660Vrms, find the power factor at the source. 10. A balanced source supplies power to three balanced loads via a power–distribution line having a per–phase impedance of . Load 1 absorbs 100kVA at pf = 0.85, lagging; Load 2 absorbs 25kVAR at pf = 0.75, leading; Load 3 dissipates 20kW at pf = 1. If the line voltage at the load is 240Vrms, find the line voltage and pf at the source. 11. A balanced Y–connected load is powered by a balanced source and draws a total of 120kW at pf = 0.8, lagging. The line voltage at the load is 208Vrms, 60Hz. a. If three 5mF capacitances are connected in parallel with the load in a Y configuration, find the power factor of the combined load. b. Repeat, but with the capacitances connected in a comment. configuration. Compare and