* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eye
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
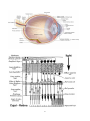
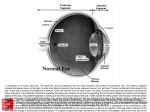
Histology Lec-13- Ass. Lec. Dentistry College Wafaa H. M. Alhashimy Second Stage Organ of special senses Part 2 : Eye Histology Each eye ball is surrounded by three distinct layers:1. An outer, fibrous (corneoscleral coat), including the sclera and the cornea 2. The uvea: a middle vascular layer including the choroid, the ciliary body and iris. 3. The inner retina. The internal cavity of the eye is filled with the vitreous body, a transparent gel that supports the shape of the eye. The corneoscleral coat The cornea covers the anterior one sixth of the eye, and is continuous with the sclera posteriorly.The sclera consists of connective tissue layer is composit of collagen fiber. The Uvea Is vascular layer , consists mainly of three layers : 1- the choroid : contains numerous blood vessels that nourish the photoresptor cells in retina and the structure system of the eyeball. 2-the ciliary body: Just posterior to the corneoscleral junction. The layers of the ciliary body include : *the stroma divided into 2 layers: 1. The outer ciliary muscle, which alters the shape of the lens in accommodation. 2. An inner vascular region extending into the ciliary process *The epithlium is double layered: a-the deeper layer is pigmented (like the retinal pigment epithelium) b-The superficial, non-pigmented epithelial layer secretes aqueous humour, which passes into the anterior chamber of the eye . 1 3-The iris : partially covers the lens and is colored portion of the eye, extends over the anterior surface of the lens from the anterior border of the ciliary body. A double layer of pigmented epithelium also circular and radial smooth muscle fibers form an opening toward the pupil. When the circular muscles contract they make the pupil smaller, when the radial muscles contract they make the pupil wider. Zonules (suspensory ligaments) : is a ring of small fibers. It connects the lens to cilliary body and allows the lens to change shape. Pupil : is hole at the center of the iris located in front of the lens. The Retina 1. The outer retinal pigment epithelium that sits on the choroid, consisting of cuboidal melanin-containing cells. 2. The inner, neural retina, containing photoreceptor cells. Layers of the retina, from the outside inwards Retinal Pigment Epithelium Melanin containing cells Layer of rods and cones Slender rods and thicker cone segments of photoreceptor cells External (Outer) limiting membrane Formed by the processes of neuroglial cells called Müller’s cells Outer nuclear layer Cell bodies of rods and cones and outer processes of Müller’s cells Outer plexiform layer 1st synaptic layer, between photoreceptors and horizontal, amacrine and bipolar cells Inner nuclear layer Cell bodies of horizontal, amacrine, bipolar and Müller’s cells Inner plexiform layer 2nd synaptic layer, between horizontal, amacrine and bipolar cells and ganglion cells 2 Ganglion cell layer Cell bodies of ganglion cells Layer of optic nerve fibres Processes of ganglion cells travelling to the brain Internal (Inner) limiting membrane Composed of the basal lamina of Müller’s cells Cone s less sensitive to light than rod cells, there are about 6_ 7 million cones in a human eye and are most concentration toward the macula the cone able to perceive finer detail and more rapid changes in images, because their response times to stimuli are faster than rod cells. There are 3 type of cone: 1- L-cone (Long – wavelengths) :peaking at reddish color. 2- M-cone (Medium – wavelengths) :peaking at green color. 3- S-cone (Short – wavelengths) :peaking at bluish color The posterior wall of the eye is the macula lutea and the optic papilla. The macula lutea is small, yellow-pigmented spot with a shallow, central depression, called the fovea, is the area of greatest visual acuity in the eye. The center of the fovea is contain cone cells. The optic papilla is the region when the optic nerve leaves the eyeball. The optic papilla lacks both rods and cones, and constitutes the blind spot of the eye. Chambers of the eye There are 3 chambers of the eye: 1. The anterior chamber, between the cornea and the iris 2. The posterior chamber, between the posterior surface of the iris and the lens 3. The vitreous space or vitreous body, lies between the posterior surface of the lens and the retina. They filled by vitreous humour, transparent jelly like fluid. It exerts fluid pressure that keeps the retina layers pressed together to maintain the shape of the eye and maintain sharp focus of images on the retina. The conjunctiva This is a thin, transparent mucous membrane extending from the lateral margin of the cornea, across the sclera, and covering the internal surface of the eyelids. 3 It is composed of a stratified squamous columnar epithelium, containing many goblet cells, that rests on a lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The Lens The lens is a transparent, avascular, biconvex structure that is suspended by the suspensory ligament of the lens, and has 3 components: 1. The lens capsule, produced by anterior lens cells 2. A subcapsular epithelium, a cuboidal layer of cells that is only present on the anterior surface of the lens 3. Lens fibres, derived from the subcapsular epithelial cells, which lose their nuclei and organelles to become filled with proteins called crystallins. Eyelid -The exterior layer of the eyelid is composite of thin skin . -The anterior layer of the eyelid is low stratified columnar with a few goblet cells , underlying lamina properia consist of denes of collagen connective tissue called tarsus, contain specialized sebaceous gland called tarsal gland , a secretary acini open in to central duct . -The free end of the eyelid contains eyelashe is large , long hair follicles. -Lacrimal gland is found in the margin of the eyelid produce tears . The tears contains mucus , salts and antibacterial enzyme (lysozyme). Tear duct : is small tube from the eye to the nasal cavity. Extra ocular muscles: each eye has six muscle that control its movement the lateral rectus, the medial rectus, the inferior rectus, the superior rectus, the inferior oblique and superior oblique. 4 5 6