* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
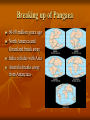
Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics accepted by the vast majority of scientists Earth’s interior is made up of two layers: the lithosphere comprising the crust and the solidified uppermost part of the mantle. Mantle is on top of the asthenosphere, a very thick viscous fluid layer Lithosphere “floats” on asthenosphere. Plate Tectonics Lithosphere broken into tectonic plates 10 major and many minor plates How Plates Move. Convection currents: heating causes a material to expand and rise, then cooling causes the material to contract and fall. Lithosphere on a metaphorical treadmill. 3 Types of Plate Boundaries 1. Transform Boundaries 2. Convergent Boundaries 3. Divergent Boundaries Convergent Boundary 2 plates moving toward each other Subduction Zone: one plate slides under another. Correlated with volcanoes. Continental Collision: if two continental plates collide. EX: Himalayan mountains Transform Boundaries Plates grind past each other. Fault line San Andreas Earthquakes Divergent Boundary 2 plates slide away from each other Mid-ocean trenches Key concept supporting plate tectonics Pangaea Super continent believed to exist during prehistoric times. Breaking up of Pangaea First major break up of Pangaea occurred during the Triassic period. Formation of Atlantic Ocean and Mississippi river occurred. Breaking up of Pangaea 150 million years ago South America break away from super continent India and Africa begin to move north Breaking up of Pangaea 60-50 million years ago North America and Greenland break away India collides with Asia Australia breaks away from Antarctica