* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plant transportation - HIS-IGSci-Bio
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
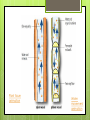
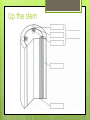
B5: Transportation Transport in Plants State the functions of xylem and phloem Flowering plants have two separate transport systems: xylem and phloem. These tissues are found throughout the plant body in roots, stems and leaves, Xylem vessels transport water and mineral ions from the roots up the stem to the leaves. Roots absorb water and mineral ions from the soil. These travel in the xylem upwards in the stem to the leaves, flowers and fruits. This is one-directional movement: from roots, via Water transport the stem, to the leaves. Water movement in plants State the functions of xylem and phloem Phloem vessels transport sucrose, amino acids and hormones to other parts of the plant. Sucrose is a soluble complex sugar Sucrose is made from the sugars made in photosynthesis and from the starch stored in roots and stems. Substances are moved in two directions in the phloem: downwards from leaves to roots upwards from leaves to flowers, fruits and buds Upwards from storage organs to new stems and leaves. Phloem loading video Plant tissue animation Water movement animation Inside a root Inside a stem Sink and source Up the stem Identify root hair cells and state their functions Roots Anchor the plant in the soil Take up water and mineral salts Root have 2 functions: hairs are microscopic Water passes into the root hair from the soil via osmosis. This process continues through all the cells until the water reaches the xylem. The xylem transports the water up the stem. Structure of root hairs: Long and thin with a large surface area. Absorption by roots Transpiration The evaporation of water from the leaves and the loss of water vapour to the atmosphere. Water only diffuses out of the leaf when the stomata are open. The flow of water up the stem relies on: Cohesion of water molecules to each other Adhesion of water molecules to the xylem Factors affecting transpiration Use your textbook p93 to summarise the factors that will affect the rate of transpiration in a plant (draw graphs if appropriate) Light Humidity Temperature Wind Page 98 – 99 complete the exam-style questions: 1 - 7