* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 - Corporate Strategy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
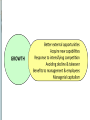
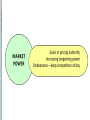
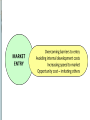
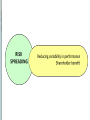
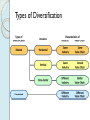
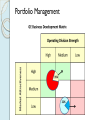
Corporate Strategy Chapter 10 Strategic Management:Value Creation, Sustainability, and Performance, 4e, 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Compare corporate strategy decisions to business level strategy decisions. 2. Historical acquisition performance and reasons why. 3. Why companies diversify. 4. Related versus unrelated diversification. 5. Why companies use either type. 6. Tools for managing diversified companies. Corporate versus Business Strategy Business strategy Value chain, Resources, Differentiation versus Low Cost approach Corporate strategy Decide which industries to enter / exit Combine divisions in Strategic Business Units Establish investment priorities across SBUs Transfer resources and management between SBUs Structure the multi-divisional company Historical Perspective on Diversification Diversification among Fortune 500 1949 …………. 30% 1974 …………. 64% 2014 …………. 89% Mergers & acquisition activity 2008: $1.5 Trillion (14% of U.S. GDP) 2015: $2.4 Trillion (12.4% of U.S. GDP) Sources: Rumelt 1982, Financial Times 2014; West 2016 Motivations for Diversification Growth Market power Market entry Risk spreading Types of Diversification Related Diversification • Achieve synergies with existing businesses • Synergies depend on fit in parts of value chain Source of Synergies Results of Synergies Market Fit Scope Operational Fit Economizing Management Fit Economizing; Resources Leverage Unrelated Diversification No synergies anticipated Depends on financial market imperfections Management identifies under-valued firms with significant growth prospects Unfavorable view of entire industry includes target firm Target firm is unable to access market financing on favorable terms Diversification Performance Wide distribution, slightly positive average Favorable Diversification Performance Selecting attractive industries Good strategic rationale Strong due diligence Capturing estimated synergies Post-acquisition integration Unfavorable Diversification Performance Acquisition premiums Poor due diligence, Bidding wars, CEO hubris, bandwagon effects Capturing estimated synergies* Loss of focus on core businesses Accelerating growth is difficult Post-acquisition integration* (* Note: also in list of favorable factors – must do these well ! ) Evaluating "Parenting Advantage" Fit Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Portfolio Management Drawbacks Evaluates SBUs on market-related factors. Value chain, extraordinary resources, core competences are less important. Static views – do not account for how resources can be shared / leveraged. BCG matrix depends on assumption that high market share is related to superior profitability – not universally true. Restructuring & Divestiture Downscoping Shedding divisions to strategically re-focus Divestiture Some of the parts are worth more than the sum of the parts Decision process for divestiture Consider same factors as for diversification, only in reverse Unattractive industry, no strategic rationale, inability to capture synergies any longer