* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Curtis Oelmann
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Backpressure routing wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
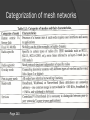
Autonomous Mobile Mesh Networks and their Design Changes Ad hoc wireless networks Set of mobile nodes that are: Self-organizing Self-healing Survivable Instantaneously available all without having infrastructure Multi-hop mesh networks Has two or more hops to any one node. These networks should also have multiple paths to get to a particular node. The data being transmitted will “hop” to each node until the data reaches its particular destination. Must be able to update the current layout of the mesh network incase a node leaves the area. Mobile Mesh Networks Autonomous Multi-hop Highly dynamic Human-centric Broadband mesh networks Categorization of mesh networks Page 240 History of the wireless network Public Safety Services Work on the 4.94 - 4.990GHz band Car accidents and first responders Surveillance-youtube.com Disaster relief Hurricane Katrina If there had been a mesh network, nodes from inside New Orleans would have been able to pinpoint where people were. With surveillance cameras mounted on telephone poles, the data would have been able to go from hop to hop transmitting data back to the first responders and police. The people we seen looting from stores would have been prosecuted because the police would have had video Defense/Military operations Easily torn down and set up On the move support Voice over ip Consumer/Home Networking New Blu-ray Dvd players Surround sound Wireless routers are limited, with multihop devices, the range is much greater. Transportation Applications I-pass Mobile mesh VS Fixed mesh networks Example of a autonomous wireless network Physical Radio Channels Commercial-off-the –shelf (COTS) Work on the 802.11 standard Allows access to many types of devices today PDA Laptops Cell phones Other home appliances Medium of Mesh networks Can work with access points connected to the internet or company intranet. Task Group S OSI layer 2 mesh ○ Called ‘Extended Service Set (ESS) Mesh Networking’ Autonomous systems can stand alone, so the discovery process is needed to find other nodes in the area that are also supporting this type of access. Routing and Multicasting We need : A way to discover if a new node has entered the group A way to update the group is a node goes down or leaves the group A way to minimize the number of hops data takes to reach the destination. A way to maximize the bandwidth being used A way to minimize power consumption by the nodes Choosing a Route On-demand The routes are established when a packet is sent. When the receiver gets a packet, they look at the route it took, and get the layout topology of other nodes in the group Proactive The nodes are continuously updating the topology by sending small packets ○ High overhead Route Reestablishment Class exercise Security Wireless eavesdropping Wal-Mart Example DOS ‘Node a’ sending countless packets to ‘node b’ could block access to other node, ‘node c’ from being able to use ‘node b’ to get to ‘node d’ IP Addressing Needs have a large set of address space IPv6 IPv4 only give 4 billion addresses ○ It is feasible for two computers to have the same address. IPv6 would give 2128 or about 3.4×1038 Helps With DAD (duplicate address detection systems) Roaming Node should be able to: Roam from one network to another Connections should be seamless Should not lose connections to data that may be critical Acquire new IP addresses instantaneously whether another autonomous mesh or a fixed mesh Applications Real time video Voice over Multi-hop mesh Instant Multimedia messaging Resource tracking Affinity group