* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Control and Grid Synchronization for Distributed Power Generation
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Intermittent energy source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Vehicle-to-grid wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
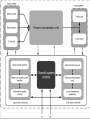
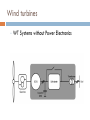
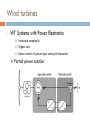
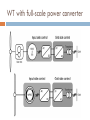
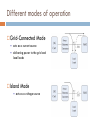
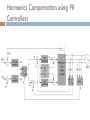
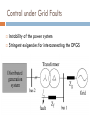
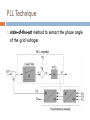
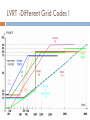
CONTROL AND GRID INTRGRATION OF DISTRIBUTED POWER GENERATION SYSTEMS M. Monfared, PhD Renewable energy sources hydropower and wind energy photovoltaic (PV) and fuel cell (FC) technology low efficiency poor controllability of the distributed power generation systems (DPGSs) based on wind and sun Source: Renewables 2011 - GLOBAL STATUS REPORT Causes DPGS Control 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Source-side controller -extract the maximum power from the input source Grid-side controller control of active power generated to the grid control of reactive power transfer between the DPGS and the grid control of dc-link voltage ensure high quality of the injected power grid synchronization Topologies of DPGS Photovoltaics and Fuel Cells – similar topology Wind Turbines – topology dependent on generator Wind turbines • WT Systems without Power Electronics Wind turbines • WT Systems with Power Electronics Increased complexity Higher cost Better control of power input and grid interaction Partial power solution WT with full-scale power converter Different modes of operation Grid-Connected Mode acts as a current source delivering power to the grid and local loads Island Mode acts as a voltage source Control Structures for Grid-Connected DPGS Two cascaded loops (Multiloop PI/PR Control) fast internal current loop, regulates the grid current an external voltage loop, controls the dc-link voltage or the active power transferred to the grid Good performance under linear loads Reference Frames X xa axb a 2 xc a e j 2 3 t d 0 dq –Control (Park transformation) synchronous (rotating) reference frame PI controller dq –Control example proportional–integral (PI) controllers to improve the performance, cross-coupling terms and voltage feedforward are used ab-Control (Clarke transformation) stationary reference frame PR (proportional –resonant) controller ab-Control example PR controllers -very high gain around the resonance frequency Natural Frame Control (abc control) PI controller PR controller nonlinear controllers PI and PR controller in abc Frame Power Quality control Harmonics Compensation Using PI Controllers Harmonics Compensation using PR Controllers Harmonic compensation by cascading several generalized integrators tuned to resonate at the desired frequency Harmonics Compensation using PR Controllers Control under Grid Faults Instability of the power system Stringent exigencies for interconnecting the DPGS 1) Symmetrical fault (no phase shifting) - rare 2) Unsymmetrical fault Control Strategies under Faults Unity Power Factor Control Strategy Positive-Sequence Control Strategy Constant Active Power Control Strategy Constant Reactive Power Control Strategy Grid Synchronization Methods Zero-Crossing Method simplest implementation Poor performance (harmonics or impulse disturbances) Grid Synchronization Methods Filtering of the grid voltages in different reference frames dq or αβ and using arctangent difficulty to extract the phase angle (grid variations or faults) PLL Technique state-of-the-art method to extract the phase angle of the grid voltages Better rejection of grid harmonics and any other kind of disturbances Problem to overcome grid unbalance IEEE 1547 IEEE 1547 Standard for Interconnecting Distributed Resources with Electric Power Systems This document provides a uniform standard for interconnection of distributed resources with EPSs [Electric Power Systems]. It provides requirements relevant to the performance, operation, testing, safety, and maintenance of the interconnection. LVRT -Different Grid Codes !