* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Major Power Grid Components
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Overhead power line wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Vehicle-to-grid wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
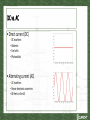
Power Systems Last edited: Monday, June 1st, 2015 Before Power Distribution • Technology developed 50-100 years before power distribution to the public: • Batteries • Arc Lights • Incandescent Lights • Electric Motors (vacuum pump) DC vs. AC • Direct current (DC) – DC machines – Batteries – Fuel cells – Photovoltaic • Alternating current (AC) – AC machines – Power electronic converters – 60 Hertz in the US Brush Electric Company • HVDC distribution that transmitted over longer distances to one customer • Niagara Falls to Buffalo • Simple distribution system that could only power arc lights Edison Electric Company • Low voltage direct current system • Better lightbulb • Safer • Short range use • Powered Small DC motors • Features added • Electric meter • Distribution System Westinghouse Electric Company • Low and High Voltage Alternating Current system • Long distance transmission • Able to change voltage • Compatible with Edison Bulb • Developed Westinghouse Bulb • Own patent for AC Motor Grid Expansion • Grid distribution networks expanded until around 1915. • The smaller grids slowly integrated into one system by connecting the distribution grids by transmission lines. • More transmission lines were added during the 1930s as part of the Depression projects and rural areas received electricity • By the 1960’s the gird was largely intact and upgrades occurred to make the lines more reliable. Major Power Grid Components • Generation • Transmission – 115 kVolts 765 kVolts – Networked • Distribution – 4 kVolts to 69 kVolts – Radial • Load Major Power Grid Components All power systems have three major components: Generation, Transmission/Distribution, and Load. Generation: Creates electric power. Transmission/Distribution: Transmits electric power from generation to load. Load: Consumes electric power. Power in = Power Out The Electric Grid Model Interconnections AC Transmission Grid DC Transmission Components Transmission & Distribution Transmission Distribution networked connections radial connections power can be supplied from power moves in one direction multiple sources only typically higher voltages, above typically lower voltages, below 100 kV 100 kV mostly overhead, with some most new construction is underground, especially in underground in urban areas suburban and urban locations often source of large-scale the source of most blackouts, blackouts but these are local Synchronism Since most generation is from synchronous machines, the interconnected power system swings together. 16 North American Control Areas