* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bauplan and Morphogenesis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
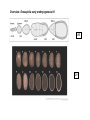
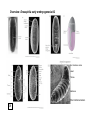
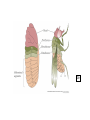
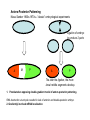
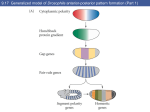
Bauplan and Morphogenesis Drosophila early embryonic development: •maternal and zygotic gene activity patterns in the early embryo. •antero-posterior patterning •dorso-ventral patterning Dr. Don Newgreen [email protected] Refs. from: Wolpert, Beddington, Jessell, Lawrence, Meyerowitz and Smith (2002) “Principles of Development” 2nd edition (Oxford University Press) Gilbert (2003) “Developmental Biology” 7th edition (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA) Also: Alberts, Johnson, Lewis, Raff, Roberts and Walter (2002) “Molecular Biology of the Cell” 4th edition (Garland Science, New York) Nüsslein-Volhard and Wieschaus (1980) Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287:795-801 Lawrence (1992) The making of a fly (Blackwell Scientific Publishing) Pattern formation : “The process by which spatial and temporal patterns of cell activities is organized within the embryo so that a well-ordered structure develops.” – Wolpert p.10 Development of a body plan, axes (rostral) (caudal) Wolpert: “The early development of Drosophila is probably the best understood developmental system of all animals, at the molecular level. This is due largely to a saturation mutagenesis screen for embryonic pattern defects carried out in the 1970s by C. NussleinVolhard and E. Wieschaus. Approximately 100 genes were identified which can account for most of the pattern formation and morphogenetic events of the early embryo. This set of genes complement a different set of genes studied by E. Lewis, whose activities were involved in specifying the identity of segments observable in the adult fly. Together, these genes became the Rosetta stones that allowed fly development to be deciphered. At the time, no one suspected that they would provide the keys to understanding development in all animals, yet that is what has occurred; even humans use the genetic networks first discovered in flies, albeit in sometimes very different ways. For this reason, Drosophila development deserves special attention in studies in developmental biology.” Overview: Drosophila early embryogenesis #1 W5 G9 Overview: Drosophila early embryogenesis #2 Ant. terminus:acron Head Thorax Abdomen Post. terminus:telson G9 G9 Similarities between Insects and Vertebrates •Many common genes/molecules •Maternal “determinants” in oocyte •Nuclear and cell division •“Mid-blastula transition”—slow down of nuclear/cell division •Molecular gradients and signals •Antero-posterior patterning •Dorso-ventral patterning •Morphogenetic movements—eg. gastrulation (Apparent) Differences between Insects and Vertebrates •Syncytial blastoderm in insects vs cellular blastoderm in verts. •Gradients within single cytoplasm vs gradients between cells •Insects are upside down (or maybe we are?) Nuclear division and cell division (cleavage) NOT necessarily synchronised 1:1. Cleavage influenced by: • amount and position of yolk (yolk impedes cleavage). •other molecules that govern angle of microtubular mitotic spindle Species variations in these means that there are many detailed cleavage patterns G8 Antero-Posterior Patterning Klaus Sander 1960s-1970s---”classic” embryological experiments Ligation of embryo to produce 2 parts A M P A P The later the ligation, the more larval middle segments develop. 1. Postulated an opposing double-gradient model of antero-posterior patterning. RNA destruction at ant pole resulted in lack of anterior and double-posterior embryo. 2. Gradient(s) involved mRNA localisation. Maternal effect genes: mutations in the mother produce patterning defects in the offspring. Christianne Nüsslein and Eric WieschausNobel Prize 1995 W5 Anterior… Bicoid mutants have A-P defects: double posterior Bicoid is a transcription factor. G9 G9 Bicoid mRNA and protein is at right time and place to affect A-P pattern (A ⋄ P gradient). W5 Bicoid mRNA “rescues” Bicoid mutants. G9 Posterior… Nanos mRNA and protein with P⋄ A gradient. Nanos protein is a translation repressor. Caudal protein with P⋄ A gradient. Caudal is a transcription factor. P A G9 W5 Putting A and P determinants together….. Zygotic hunchback hunchback mRNA Hunchback protein G9mod Making and holding the A-P gradients in a syncytium…. G9 Termini: Torso (RTK) signalling. Note: Torso activation has different outcomes in Bicoid and Caudal contexts. Former leads to acron formation, latter leads to telson formation. G9 (Groucho) End lect #1