* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download audio amplifier - Kaushik Science Projects
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Videocassette recorder wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Compact disc wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Antique radio wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Mixing console wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Sound reinforcement system wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Home cinema wikipedia , lookup
Cambridge Audio wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
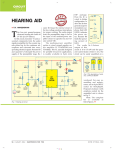
AUDIO AMPLIFIER USING IC 6283 Intoduction This is a very useful and simple circuit diagram for amplifying weak signal from a capacitive condenser microphone. You can use this circuit for sound sensing applications and some automatic robotic sensors. We have already posted an efficient audio amplifier circuit using 6283 IC, it is somewhat complicated and is suitable for very sensitive applications. But this condenser microphone DIY audio sound amplifier is very small and simple to implement because it uses only two BC547 transistors and some discrete components. You can construct this circuit with a minimum price of $2. This circuit is apt for cheap amplification purposes in electronics such as pre amplifier for FM transmitters. Circuit diagram Components required 1. Resistors (2.2kΩ; 3.3kΩ; 470kΩ; 220kΩ; 1.2kΩ) 2. Capacitors (0.1µF x 2; 10µF,16V) 3. Transistors (BC547 x 2) 4. Condenser mic 5. Speaker (8Ω, ½ Watt) Working of amplifier The circuit is alienated into three divisions: Condenser mic, audio amplifier and loudspeaker. Condenser mic is a type of capacitive audio sensor (audio transducer) that converts the sound (audio) signal into electrical signals. These electrical signals are too weak so it is amplified by the amplifier unit. The amplified output is obtained across the speaker. The output of condenser mic is coupled via a coupling capacitor of 0.1µF, the purpose of this capacitor is to remove DC contents in the audio signal. A 2.2kΩ resistor is used to give the required biasing to the condenser microphone. Transistor Q1 is configured as collector to base biasing mode. This is accomplished via 470kΩ resistance. This resistor provides negative feedback to the transistor Q1. The output of Q1 becomes available at the collector (across 3.3kΩ resistor), which is the input to the transistor Q2 via a 0.1µF capacitor. The capacitor removes DC voltages due to the biasing of Q1. Transistor Q2 is configured as fixed bias using a 220kΩ resistor. It also provides further amplification. The amplified output from Q2 is available across the 1.2kΩ resistor. The 10µF electrolytic capacitor also used to block the DC voltages associated with the biasing of transistor Q2. Use a 8Ω, ½ watt speaker to hear the amplified signal. ––