* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11. Legacies of the Great War
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
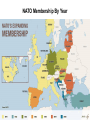
Lesson 11 Legacies of the Great war History, Geopolitics and International Affairs Headline Associated Press, January 25, 2015 The Baltic States NATO Members NATO Membership By Year Why Did Europe Go to War in 1914? What was the power environment in Europe in 1914? Balance of Power International situation where no one state is strong enough to dominate all others. Balance of Power 1914 Europe 1914 Phases of World War I 1914 - Maneuver and Frustration 1915 - Search for New Solutions 1916 - Attrition 1917 - Desperation and Anticipation 1918 - Dénouement Causes of WW I Nationalism Militarism Interlocking Alliances 11 Causes of WW I Nationalism • Strong sense of bond among people • Common language, culture, identity • France, Germany, Balkans Power Politics At Work 12 Causes of WW I German Nationalism 1866-1871 German States – 1740-1866 13 Causes of WW I German Nationalism Germany came “late to the European table” Sought her legitimate “place in the sun” 14 Causes of WW I Nationalism Militarism • Belief that a strong military is critical to the security and prosperity of a nation • Military considerations paramount • Dominate government, particularly diplomacy • Fed by success of Prussia/Germany 15 Causes of WW I Nationalism Militarism Interlocking Alliances 16 Alliances 1839: Treaty of London (Britain guaranteed Belgian neutrality) 1879: Dual Alliance (Germany & Austria-Hungary) 1882: Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy) • secret pact 1894: Dual Entente (France, Russia) 1904: Entente Cordiale (France, Britain) 1907: Triple Entente (France, Britain, Russia) 17 Alliances of 1914 Triple Alliance Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy • Italy did not go to war in 1914 • Germany - Austria-Hungary Central Powers Triple Entente France, Britain, Russia • Became core of the Allied Powers 18 Major Power Strategic Goals Why did each of the powers go to war? 19 Major Power Strategic Goals France Revanche (revenge) The humiliation of the Franco-Prussian War “Think of it always, speak of it never.” 20 Major Power Strategic Goals France Revanche (revenge) Natural Frontiers Germany “Place in the sun” Austro-Hungary Expand into Balkans Russia Re-establish itself after 1905 defeat Expand into Balkans Great Britain Maintain European balance of power 21 The World At War 22 Timetable to War May 7, 1915 Lusitania sunk Mar 15, 1916 Army Reorganization Act Dec 1916 Wilson begins peace initiative Jan 22, 1917 Wilson calls for peace without victory Feb 1, 1917 Germany resumes unrestricted sub warfare Feb 3, 1917 US breaks relations with German Feb 24, 1917 Zimmerman Telegram revealed Apr 2, 1917 Wilson asks for war declaration Declaration of War Declaration of War April 2, 1917 President Wilson asked Congress for declaration of war April 4, 1917 Senate approved 82 – 6 April 6, 1917 House approved 373 - 50 Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted submarine warfare • US tradition of defending Freedom of the Seas Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted submarine warfare The Zimmerman Telegram • Attempt at strategic diversion by Germany Zimmerman Telegram Sent by German Foreign Secretary, Arthur Zimmerman • To Embassy in Washington, January 16, 1917 Ambassador forwarded to Embassy in Mexico British intercepted message, passed to US Publication of message enflamed US! Zimmerman Telegram Berlin, January 19, 1917 On the first of February we intend to begin submarine warfare unrestricted. In spite of this, it is our intention to endeavor to keep neutral the United States of America. If this attempt is not successful, we propose an alliance on the following basis with Mexico: That we shall make war together and together make peace. We shall give general financial support, and it is understood that Mexico is to reconquer the lost territory in New Mexico, Texas, and Arizona. The details are left to you for settlement.... You are instructed to inform the President of Mexico of the above in the greatest confidence as soon as it is certain that there will be an outbreak of war with the United States and suggest that the President of Mexico, on his own initiative, should communicate with Japan suggesting adherence at once to this plan; at the same time, offer to mediate between Germany and Japan. Please call to the attention of the President of Mexico that the employment of ruthless submarine warfare now promises to compel England to make peace in a few months. Zimmerman (Secretary of State) Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted submarine warfare The Zimmerman Telegram • Attempt at strategic diversion by Germany • Posed a direct threat to the U.S. • Challenged Monroe Doctrine • Revelation focused Americans on war issue Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted submarine warfare The Zimmerman Telegram Make the World Safe for Democracy • Democracy vs. Autocracy Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted submarine warfare The Zimmerman Telegram Make the World Safe for Democracy American “Non-Neutrality” • Trade with belligerents, mostly Britain Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted submarine warfare The Zimmerman Telegram Make the World Safe for Democracy American “Non-Neutrality” American Frustration • Lack of response to peace feelers Why Did The US Enter the War? Another view A. J. P. Taylor (British historian) The First World War: An Illustrated History (1963) German submarines forced the United States into the war. But it would be too simple to say that America fought solely for the freedom of the seas, still less of course for the sake of New submarines Mexico. The United States were committed to the Allied side. German forced thealready United States into the war. But it would be too simple to say that America fought solely for the freedom of the seas, still less of course for the sake of New Mexico. The United States were already committed to the Allied side. Why Did The US Enter the War? Another view A. J. P. Taylor (British historian) The First World War: An Illustrated History (1963) German submarines forced the United States into the war. But it would be too simple to say that America fought solely for the freedom of the seas, still less of course for the sake of New Mexico. The United States were already committed to the Allied side. At first, the American Government had tried to remain strictly neutral. Banks were instructed to give credit to theGovernment belligerents. Soonhad businessmen At first,not the American tried tocomplained remainthat the chances of good profits were being lost. strictly neutral. Banks were instructed not to give credit to the belligerents. Soon businessmen complained that the chances of good profits were being lost. Why Did The US Enter the War? Another view A. J. P. Taylor (British historian) The First World War: An Illustrated History (1963) German submarines forced the United States into the war. But it would be too simple to say that America fought solely for the freedom of the seas, still less of course for the sake of New Mexico. The United States were already committed to the Allied side. At first, the American Government had tried to remain strictly neutral. Banks were instructed not to give credit to the belligerents. Soon businessmen complained that the chances of good profits were being lost.extended to the Allies. Copper, cotton, Large funds were wheat poured across the Atlantic. Factories worked overtime on British and French Large funds were extended to the Allies. Copper, cotton, orders. The economy boomed. wheat poured across the Atlantic. Factories worked overtime on British and French orders. The economy boomed. Why Did The US Enter the War? Another view A. J. P. Taylor (British historian) The First World War: An Illustrated History (1963) German submarines forced the United States into the war. But it would be too simple to say that America fought solely for the freedom of the seas, still less of course for the sake of New Mexico. The United States were already committed to the Allied side. At first, the American Government had tried to remain strictly neutral. Banks were instructed not to give credit to the belligerents. Soon businessmen complained that the chances of good profits were being lost.extended to the Allies. Copper, cotton, Large funds were wheat poured across the Atlantic. Factories worked overtime on British and French orders. The economy boomed. If the German submarines stopped this trade, there would be depression, crisis. If the Allies lost the war, the American loans would be lost also. If the German submarines stopped this trade, there would be depression, crisis. If the Allies lost the war, the American loans would be lost also. Why Did The US Enter the War? Another view A. J. P. Taylor (British historian) The First World War: An Illustrated History (1963) German submarines forced the United States into the war. But it would be too simple to say that America fought solely for the freedom of the seas, still less of course for the sake of New Mexico. The United States were already committed to the Allied side. At first, the American Government had tried to remain strictly neutral. Banks were instructed not to give credit to the belligerents. Soon businessmen complained that the chances of good profits were being lost.extended to the Allies. Copper, cotton, Large funds were wheat poured across the Atlantic. Factories worked overtime on British and French orders. The economy boomed. If the German submarines stopped this trade, there would be depression, crisis. If the Allies lost the war, the American loans would be lost also. In the end, the United States went to war so that America could remain prosperous and rich. Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted submarine warfare The Zimmerman Telegram Make the World Safe for Democracy American “Non-Neutrality” American Frustration Protect US Economic Interests Grand Strategy 101 Why did Great Britain go to war in 1914? Maintain European balance of power 1917: Britain, France on the ropes Russia in revolution, almost out of the war Germany poised to knock Britain out of the war w/ subs US chose to pursue maintain balance WhatBritish shouldobjective: the US do? Why Did The US Enter the War? Unrestricted Submarine Warfare The Zimmerman Telegram Protect US Economic Interests Make the World Safe for Democracy Maintain European Balance of Power American “Non-Neutrality” American Frustration Protect US Economic Interests Maintain European Balance of Power Next: Lesson 12 Legacies of the Great war History, Geopolitics and International Affairs Title Title