* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Procedure for Part A: Simple Circuit
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
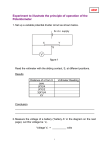
SNC1DI Name: __________________ Partner: __________________ Date: __________________ Lab Activity: Measuring Voltage and Current in a Simple Circuit Materials: 9V battery 2 light bulbs 1 voltmeter 1 ammeter 8 wires Procedure for Part A: Simple Circuit 1. Before building your circuit, measure the voltage across the battery. To do this, connect the negative terminal of the battery to the black negative terminal of the voltmeter. Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the red positive terminal of the voltmeter (use the 15V scale throughout this lab activity). Since you are using the same battery throughout this activity, record the voltage at the source in Tables 1, 2, and 3. Disconnect the voltmeter from the battery. 2. Build a simple circuit as follows: Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the black negative terminal of ammeter. Connect positive red terminal of ammeter (use the 500mA scale throughout this lab activity) to a light bulb (attach to screw) Connect other side of light bulb (other screw) to a switch. Connect the switch back to the positive terminal of the battery. 3. Close the switch. Note the brightness of the bulb. Is it very bright, bright, dim, or very dim? 4. Read the ammeter, and record the current of this circuit in Table 1. Be careful you read the scale correctly! 5. Connect the voltmeter across the light bulb to measure voltage drop. Make sure the negative terminal of the voltmeter is connected to the more negative end of the light bulb (and positive to positive). Record voltage drop in Table 1. 6. Open the switch. Draw a circuit diagram of this circuit in the box below Table 1. Include the voltmeter and ammeter in your diagram. LEAVE THIS CIRCUIT INTACT WHEN MOVING ON TO PART B. Observations for Part A: Brightness of Bulb: _____________________________________ Table 1: Current and Voltage for a Simple Circuit Voltage at Source (V) Circuit Diagram: Current (mA) Voltage Drop at Bulb (V) Procedure for Part B: Series Circuit 1. Add a second bulb to the simple circuit in Part A by connecting it in series (connect it between the first bulb and the switch). 2. Close the switch. Note the brightness of the bulbs. Are the bulbs brighter, dimmer or the same brightness compared to when there was only one bulb? 3. Read the ammeter, and record the current of this circuit in Table 2. Since this circuit has only one path, the current will be the same at every point in this circuit. 4. Connect the voltmeter across the first light bulb to measure voltage drop. Repeat for the second light bulb. Record your values in Table 2. 5. With switch closed, unscrew one bulb. Record your observations then screw the bulb back down. 6. Open the switch. Draw a circuit diagram of this circuit in the box below Table 1. Include one ammeter and one voltmeter in your diagram. Observations for Part B: Brightness of bulbs: ________________________________________________________________ What happens when one bulb is unscrewed? ___________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Table 2: Current and Voltage for a Simple Circuit Voltage at Source (V) Current (mA) Voltage Drop at Bulb 1 (V) Voltage Drop at Bulb 2 (V) Circuit Diagram: Procedure for Part C: Parallel Circuit 1. Remove the second bulb from your circuit, and reconnect the first bulb to the switch so you have the simple circuit you built in Part A. 2. Add the second bulb in parallel with the first bulb. 3. Close the switch. Note the brightness of the bulbs. Are the bulbs brighter, dimmer or the same brightness compared to when there was only one bulb? 4. Read the ammeter, and record the current at the source in Table 3. 5. Disconnect the ammeter (connect the battery directly to the first bulb). Connect the ammeter along the path of the second light bulb. Record the current at bulb 2 in Table 3. 6. Connect the voltmeter across the second light bulb to measure voltage drop. Record in Table 3. 7. With switch closed, unscrew one bulb. Record your observations then screw the bulb back down. 8. Open the switch. Draw a circuit diagram of this circuit in the box below Table 3 (include meters). Observations for Part C: Brightness of bulbs: _____________________________________ What happens when one bulb is unscrewed? ___________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Table 3: Current and Voltage for a Simple Circuit Voltage at Source (V) Current at Source (mA) Current at Bulb 2 (mA) Voltage Drop at Bulb 2 (V) Circuit Diagram: Discussion Questions (please answer in complete sentences): 1. a) In Part A, how did the voltage at the source compare to the voltage drop at the bulb? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ b) In this circuit, what energy conversion is occurring at the load? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 2. a) Compare the current in Part A (see Table 1) to the current in Part B (see Table 2). How does adding a second bulb in series affect the current in the circuit? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ b) Why does adding another load in series affect the current in this way? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 3. a) Compare the voltage drop across the bulb in Part A (see Table 1) to the voltage drop across the bulbs in Part B (see Table 2). How does adding a second bulb in series affect the voltage drop across each load? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ b) Why does adding another load in series affect voltage drop in this way? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 4. Is there a relationship between voltage drop and brightness of a bulb? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 5. a) Compare the current in Part A (see Table 1) to the current at the source in Part C (see Table 3). How does adding a second bulb in parallel affect the current coming from the source? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ b) Why does adding another load in parallel affect the current in this way? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 6. In Part C (parallel circuit), how does the current going through the second bulb compare to the current at the source? Explain your observations. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 7. Consider this statement: “Under ideal conditions, the voltage drop across each bulb in a parallel circuit should equal the voltage at the source.” a) Based on your knowledge of parallel circuits, explain why the statement makes sense. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ b) Describe whether or not your results support the statement above (see Table 3). If not, why do you think your results are different? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________