* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Voltage Sensor ML17f - CMA
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Geophysical MASINT wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
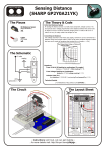
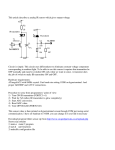
VOLTAGE SENSOR ML17F USER’S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The Voltage sensor ML17f is designed for exploring the basic principles of electricity. With a wide input voltage range of – 15 to +15 V this sensor can be used to measure voltages in AC and DC circuits. The sensor is equipped with two 4-mm banana plugs and two additional alligator clips are delivered with the sensor. The sensor has differential inputs, which means that measurements can be done directly across circuit elements without the constraints of common grounding. It can be used to measure positive potentials, as well as negative potentials. The sensor should be connected parallel to a circuit element to measure the potential difference across the element. The sensor is provided with over-voltage protection and voltages up to ± 30 V (related to ground) will not damage the sensor. It never can be used for higher voltages or 220 V. The Voltage sensor is an I2C digital sensor, which gives calibrated values of the measured quantity. This sensor can only be connected to special interfaces that support I2C digital sensors like the CMA MoLab interface. The sensor cable needed to connect the sensor to an interface is not supplied with the sensor (sensor cables are supplied with interfaces). Sensor specifications For sampling rates up 1 kHz (1000 samples per second) the Voltage sensor works as a digital sensor and converts the measured voltage to a digital value via 14-bit analogto-digital conversion. For sampling rates above 1 kHz the sensor works as an analog sensor. The analog signal generated by the sensor (on its ADC pin) is read by the connected interface and is converted to a digital value by the 12-bit AD converter on the interface. The maximum sampling rate of the sensor is 100 kHz (samples per second). Practical information CAUTION: NEVER use high voltages or household AC. The Voltage sensor is used to measure the potential difference between the ends of an electrical component and is therefore connected across (i.e. in parallel) the component. Make sure you observe the correct polarity i.e. connect the black lead from the Voltage Sensor to the negative terminal of the cells, otherwise the sensor will give readings with the wrong sign. The Voltage Sensor(s) can be used in conjunction with a Current sensor(s) anywhere in a circuit. 2 | ML17f Voltage Sensor User’s Guide For reasons of accuracy, if more than one Voltage sensor is being used in a circuit, ensure they share a common earth (connect their black leads to each other). Collecting data The Voltage sensor works only with specific interfaces. The sensor will be automatically detected when connected to such an interface. For detailed information about measurements with sensors consult the User Manuals of the interface and the Coach 6 software. Calibration The Voltage sensor is supplied with a factory calibration in volt (V). The Coach 6 program allows shifting the pre-defined calibration or creating a new two-point linear calibration if needed. The user calibration is stored in non-volatile user sensor memory. Suggested experiments The Voltage sensor can be used in various experiments such as: Charging and discharging capacitors. Characteristics of a light bulb and a diode. Measurements of internal resistance and EMF. Measurements in series and parallel electrical circuits. Together with a Current Sensor it can be used to explore the relationship between the current and the voltage in electrical circuits. Figure 2. Measuring a battery voltage. Figure 2. Measuring the voltage during charging and discharging a capacitor. ML17f Voltage Sensor User’s Guide | 3 Technical Specifications Sensor kind Up to 1000 Hz - digital (on-sensor analog to digital conversion) (14-bits resolution, communication via I2C) Above 1000 Hz - analog (on-interface analog to digital conversion) Measuring range Differential -15 .. +15 V Resolution Typical ± 2 mV, Maximal ± 3 mV Accuracy Typical ± 0.3 % and Maximal ± 1 % at full range Max. over voltage protection ± 30 V Input impedance 5.3 ± 1.5% MΩ at 25°C Zero offset Zero-voltage offset drift: typical ± 1 mV at 25°C Maximal sampling rate 100 kHz Sensor dimensions Housing: 42 x 18 x 16 mm Electric cords: length 35 cm; diameter 3 mm Connection 5-pins mini jack plug Warranty: The Voltage sensor ML17f is warranted to be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of 12 months from the date of purchase provided that it has been used under normal laboratory conditions. This warranty does not apply if the sensor has been damaged by accident or misuse. Note: This product is to be used for educational purposes only. It is not appropriate for industrial, medical, research, or commercial applications. Rev. 15/05/2013 4 | ML17f Voltage Sensor User’s Guide