* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download gingival enlargement
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
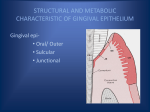
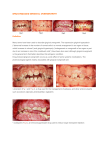
• • • • • • • • • • • INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION DRUG INDUCED GINGIVAL ENLARGEMENT ETIOPATHOGENESIS DIAGNOSIS SYMPTOMS CLINICAL PRESENTATION TREATMENT RISK FACTORS PROGNOSIS PREVENTION INTRODUCTION Terminology Gingival enlargement Hypertrophic gingivitis Gingival hyperplasia. GINGIVAL ENLARGEMENT Gingival enlargement refers to excessive growth of the gums, and may also be known as gingival hyperplasia or hypertrophy. CLASSIFICATION 1. Inflammatory enlargement a. Chronic b. Acute 2. Drug induced enlargement 3. Enlargement associated with systemic diseases or conditions a. Pregnancy b. Puberty c. Vitamin c deficiency d. Plasma cell gingivitis e. Non specific conditioned enlargement (pyogenic granuloma) 4. specific diseases causing gingival enlargement a. Leukemia b. Granulomatous diseases 5. neoplastic enlargement a. Benign tumors b. Malignant tumors 6. false enlargment Drug-induced enlargement • Drug-induced gingival overgrowth occurs as a side effect of some systemic medications. (such as phenytoin, phenobarbital, lamotrigine, valproate, vigabatrin, ethosuximide, topiramate and primidone) , such as nifedipine and verapamil.the dihydropyridine derivative isradipidine can replace nifedipine and does not induce gingival overgrowth. , cyclosporine Age Dose Duration Saliva conc. Serum conc. Demograph ic variables Drug HLA Antigen Genetic predisposit ion Chronic irritation Genetic markers Oral hygiene Hormones Molecular &cellular changes Pharmaco kinetic variables Diagnosis The diagnosis of drug-induced gingival overgrowth is mainly based on : Clinical appearance Medical history Histopathological features • • • • Discomfort Interfere with speech or chewing Halitosis (bad odour to the breath) Look unsightly CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Normal gingiva Gingival enlargement Clinical presentation • Painless beadlike enlargement of IDP • Extend to marginal gingiva • Massive tissue fold covering tooth crown Continue… • Mulberry shaped, firm, pale pink, resilient, lobulated surface, no tendancy to bleed. • When complicated by inflammation,: red/bluish red color,obliterate the surface demarcation, tendency to bleed • Onset within 3 months • Predilection for anterior gingiva , a drug used for the management of epilepsy, 50 to 100% of treated patients can occur Male patients are at high risk Continue… • Phenytoin analogues(1-allyl-5phenylhydantoinate & 5-methyl-5phenylhydantoinate) • Accumulation of gingival fibroblasts • Decreased collagen degradation • Accumulation of connective tissue Continue… • Enlargement is Independent of local inflammation • Also Precipitate megaloblastic anemia & folic acid deficiency , an immunosuppressant drug used to reduce organ transplant rejection 15 to 85% of treated patients can occur Male patients are at high risk cyclosporin solution experience earlier onset of gingival changes than using capsules. • • • • • Prevent organ transplant rejection Reversibly inhibit helper T cell Dosage >500 mg/day induce g.enlargement More vascularized connective tissue Enlargement is a hypersensitivity reaction • Cyclosporine+Hydroxycyclosporine • Stimulate fibroblast proliferation • Excessive extracellular accumulation • Gingival enlargement -a group of anti-hypertensive drugs 10 to 30% treated patients can occur nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem, oxodipine, amlodipine), • Increases gingival fibroblast • Increase in production of connective tissue matrix • Used in the treatment of cvs conditions, • In kidney transplantation patient along with cyclosporine Other drugs, such as antibiotics and have been also associated with this side effect. Histopathology • Pronounced hyperplasia of connective tissue & epithelium • Acanthosis of epithelium • Elongated rete pegs • Increased fibroblast, collagen, new blood vessels • Abundant amorphous ground substance. Mild gingival enlargement will often diminish with removal of plaque and calculus deposits. Mouth washes: Chlorhexidine Tooth brushing Flossing • Altering the medication • Reducing the dose • It may take from 1 to 8 weeks for resolution of gingival lesions. • CCB: amlodipine and felodipine, isradipin • Cyclosporine: tacrolimus • Phenytoin: valproic acid, carbamazepine, or phenobarbitone, vigabatrin • Patient taking cyclosporin, the azithromycin decrease the severity of gingival overgrowth • Organ transplant patients,dosages of both prednisolone and azathioprine • Gingivectomy is the treatment preferred when the • Gingival overgrowth involves small areas (up to six teeth), there is no evidence of attachment loss and • There is at least 3 mm of keratinized tissue. • The periodontal flap is preferred when the • gingival overgrowth involves larger areas (more than six teeth) and there is evidence of attachment loss combined with osseous defects • CO2 or argon-laser surgery has been proposed as surgical treatment of gingival overgrowth because of decreased surgical time and rapid post-operative haemostasis. • Good oral hygiene for preventing or retarding the recurrence of the gingival overgrowth is important after surgery. RISK FACTORS • Potential risk factors for drug-induced gingival overgrowth include the following: • • • • • • Poor oral hygiene Periodontal disease Periodontal pocket depth Gingival inflammation Degree of dental plaque Duration and dose of cyclosporine Prognosis • Recurrences are frequent, particularly in patients with less than optimal plaque control and when the drug regimens cannot be modified or reduced. Prevention may help to prevent the onset and development of gingival enlargement. • Clinical periodontology – Carranza • Periodontology and implant dentistry – Lindhe (vol 1)