* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drug Interactions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
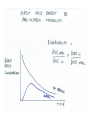
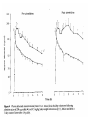
Pages 645 to 724 Mechanisms of Drug Interaction • Pharmacokinetic – – – – – – – Reduced rate and/or completeness of absorption Altered bioavailabilty Reduced plasma protein binding Altered tissue distribution Altered hepatic metabolism Altered renal excretion Haemodynamic interactions • Pharmacodynamic – – – – Potentiation/antagonism at target receptor Potentiation at non-target receptor Alteration of fluid/electrolyte environment Interference with transport mechanisms Pharmacodynamic Interactions • Decreased effectiveness • Increased toxicity • Predictable within a class of drugs Pharmacokinetic Interactions • Outcome direct effect of change in drug level • Chance of interaction occurring difficult to predict • Nature of interaction can be predicted Drugs with zero order kinetics Drugs with low bioavailability due to high pre-systemic metabolism (First pass effect Interaction in the gut Interaction in the liver Haemodynamic drug interaction Displacement from plasma protein binding sites Interaction in the kidney Interaction at the receptor NB MAOIs Things to Remember • Interactions are easily forgotten when prescribing • Interactions are difficult to remember • Pharmacodynamic interactions can often be predicted across drug classes • Pharmacokinetic interactions can not be predicted – experiments needed • Many interactions probably remain undescribed – so look out for them • The chances of interaction are 60 times higher in a patient taking 5 drugs than in one taking 2.