* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Ocular Anatomy
Fundus photography wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Macular degeneration wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
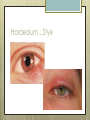
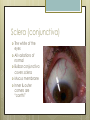
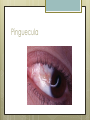
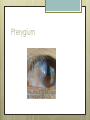
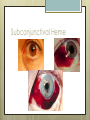
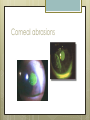
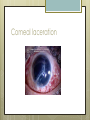
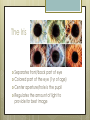
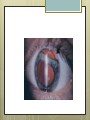
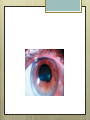
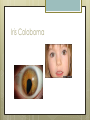
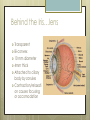
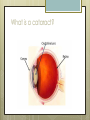
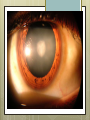
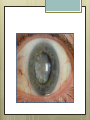
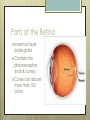
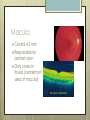
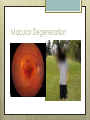
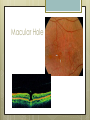
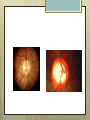
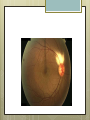
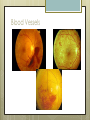
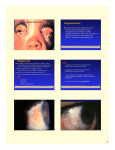
Basic Ocular Anatomy That Won’t Put You to Sleep Leslie Gallagher, OD, FAAO Lifetime Eye Holton, KS What’s In It For Me? Better understanding of duties Better patient communication Increased enjoyment of work Increased responsibilities (pay) The Eye From 10,000 Ft Like an onion…layers Not a perfect sphere Examine the eye from front (anterior) to back (posterior) Lids, Lashes Moveable folds of skin Blinks 4-6/minute Protects the eye Spreads tears (windshield wiper) Muscles control lid position/function Ptosis Blepharitis Trichotillomania Latisse Hordeolum…Stye The parts the are visible from outside Conjunctiva/sclera Iris Pupil Cornea on the outside but not visible Sclera (conjunctiva) The white of the eyes All variations of normal Bulbar conjunctiva covers sclera Mucus membrane Inner & outer corners are “canthi” What in the world is a caruncle? Pinguecula Pterygium Subconjunctival Heme Not to be confused with.. Pink Eye (conjunctivitis) Cornea Cornea Clear windshield Where is meets the sclera is called the “limbus” 70% refractive power of the eye 5 layers (epithelium, Bowman’s, stroma, Descemet’s, & endothelium) Layer’s of the Cornea Epithelium- painful when injured; heals very quickly without scarring Bowman’s- doesn’t regenerate; scars Stroma- 90% cornea thickness; scars Descemet’s- transparent, elastic Endothelium- single layer of cells; regulates (de-)hydration; does NOT regenerate Corneal abrasions Corneal Foreign Bodies Corneal laceration LASIK The Iris Separates front/back part of eye Colored part of the eye (1yr of age) Center aperture/hole is the pupil Regulates the amount of light to provide for best image Iris Coloboma Behind the Iris…lens Transparent Bi-convex 10 mm diameter 4mm thick Attached to ciliary body by zonules Contraction/relaxati on causes focusing or accomodation What is a cataract? Vitreous Clear jelly-like substance Fills the back 2/3 of the eye Gives shape to the eye Vitreous Detachment Floaters Back to the “Onion” Sclera Choroid Retina Parts of the Retina Innermost layer inside globe Contains the photoreceptors (rods & cones) Cones can discern more than 150 colors Rods- function best in dim lighting Damage to rods result in night blindness Macula Central 4.5 mm Responsible for central vision Only cones in fovea (centermost area of macula) Macular Degeneration Macular Hole Optic Nerve 2nd cranial nerve 25-30 mm long Transmits impulses from eye to brain Physiological blind spot Dr. looks at for many conditions WAKE UP!!! Blood Vessels Extra ocular Muscles 6 muscles Insertion is covered by conjunctiva Congenital Acquired- like stroke victims Summary By understanding basic ocular anatomy Better patient communication Better communication with Dr. Increased responsibility