* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ph 213 – Challenging Problems (set 6) Name: Due: August 6, 2013
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
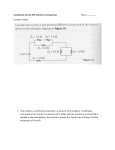
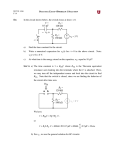
Ph 213 – Challenging Problems (set 6) Name: _______________________ Due: August 6, 2013 1. For the circuit shown at right, Let R1 = R3 = and R2 = , and E1 = 2V, E2 = E3 = 4V, you can neglect the internal resistance of all batteries. A) Calculate the current through each battery. B) Calculate the power delivered or used (specify which case) by each battery A) Let’s choose the direction of currents and travel direction around the loop as shown on the diagram. Applying the junction rule for current I1 = I2 + I3 Next apply loop rule for the two loops: 2 – 10I1 – 20I2 – 4 = 0 I1 = –2I2 – 0.2 4 + 20I2 – 10I3 + 4 = 0 I3 = 2I2 + 0.8 Insert in first equation: –2I2 – 0.2 = I2 +2I2 + 0.8 I2 = – 0.2 A (negative sign indicates the actual direction of current in R1 is to the left). And I1 = –0.2A (negative sign indicates the actual direction of current in R1 is to the left). And I3 = 0.4A B) The power delivered by battery 1 is The power delivered by battery 2 is The power delivered by battery 3 is P1 = E1 I1 P2 = E2 I2 P3 = E3 I3 is is is P1 = 2V . 0.2A = 0.4 w P2 = 4V . 0.2A = 0.8 w P3 = 4V . 0.4A = 1.6 w 2. In the circuit shown let R1 = R, R2 = 2R, R3 = R, and R4 = 3R. The switch S has been already in position 1 for a long time. Do all calculations in terms of R, C, E, and t (time) A) What is the current (including direction) through each of the four resistors? No current flows through resistor R3. A long time after the switch has been closed, capacitor will be fully charged and acts as open in circuit, so no current flows through the branch of the circuit containing the capacitor and resistor R4. So the circuit looks like the circuit diagram at right. B) Find the potential VC across the capacitor. The potential across the capacitor is the same as the potential across resistor 2. The circuit is similar to the one below VC = VR2 = R2 VC VR2 R1 R2 2 VC 3 C) Now let t = 0 when you move the switch S to position 2. Immediately after switch is moved to position 2, what is the current (include direction) through each resistor? When the switch is moved to position 2 the circuit looks like the circuit diagram shown below. The current flows counterclockwise (up from the capacitor). Because VC= (2 / 3) E and the equivalent resistance is Req= R4 + R3 = 4R, the current is I VC Req 2 3 4R I 6R D) Make a graph of current vs. time for the current that flows out of the capacitor after the switch is moved to position 2 at t = 0. Indicate the value of the current at time t = 0, t = and t = 2 on your graph. Because the equivalence resistance is Req= 4R , the time constant is τ= RC = 4RC. Recall in one time constant τ the current drops to 1/e I0 = 0.37 I0 E) After keeping the switch S in position 2 for a long time, the switch is thrown to position 1 again. Immediately after the switch has been thrown to position 1, find the current through the battery. After a long period in position (2) the capacitor is now uncharged. An uncharged capacitor in a closed circuit acts like a short. Therefore immediately after the switch has been thrown to position (1), the capacitor can be replaced by a wire, and the circuit now looks like one at right. Resistors R2 and R4 are in parallel and result in series with R1. RR I /( R1 2 4 ) R2 R4 I /( R 6R 2 5 ) 5R 11R







![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)