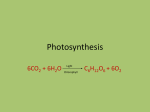
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Leaf Arrangements
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Leaf Arrangements Types of leaf arrangements include: Phyllotaxy Decussate Back to main leaf menu Alternate Basal Next Opposite Equitant Back to vegetative parts main menu Whorled Rosette Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy The spiral arrangement of leaves on the stem is called phyllotaxy. Red oak (Quercus rubra) Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy Leaves spiral around the stem in a regular pattern. It can be described as a fraction with the numerator being the number of turns around the stem and the denominator being the number of leaves it takes to return to original leaf position. 4 2 1 0 3 5 Aloe saponaria has a 2/5 phyllotaxy. It produces 5 leaves before it spirals back to the start position. Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy The vertical rank of leaves in a spiral are said to have the same orthostichy. Leaves 0 and 8 have the same orthostichy after three spirals around the axis (3/8). 7 4 3 8 0 5 6 5 1 2 Smoke tree (Cotinus) Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy Phyllotaxy indices (like many other spirals in nature) follow a Fibonacci series. The Fibonacci series consists of a series of numbers that remarkably describe many spirals observed in nature. The previous pair of numbers sum to the next number in the series. The series is 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89 … Spirals of disc florets in Purple coneflower (Echinacea). Ammonite fossil Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy Phyllotaxy follows a numerator and denominator set of offset Fibonacci numbers. 1/2, 1/3, 2/5, 3/8, 5/13, 8/21, 13/34 … A 3/8 phyllotaxy A 2/5 phyllotaxy Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy As illustrated here with the areolas and spines (modified leaves) of the cactus Mammillaria, there is actually one set of spirals in a clockwise direction and one set in a counter-clockwise direction. Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy If you start to look for these types of patterns, you will see the clockwise and counter-clockwise spirals in many different plant structures. Pineapple (Annas) fruit Back to main leaf menu Magnolia fruit Back Next Lantana inflorescence Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Phyllotaxy Phyllotaxy can also be expressed by these sets of opposing spirals. Each set of spirals is called a parastichies. Each parastichies occurs at a regular interval, but opposite spirals occur in a different number and a different interval. In this example, there is 1 turn and 3 leaves in the clockwise direction and 3 turns with 8 leaves in the counter-clockwise direction. Back to main leaf menu Back Next Tradescantia Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Alternate- single leaf per node In the alternate arrangement, a single leaf is attached at each node. The leaves may be arranged in straight rows or spiral around the stem. The spiral arrangement of leaves on the stem is called phyllotaxy. 4 2 1 Node Back to main leaf menu 5 3 Leaf Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Alternate- single leaf per node There are a few plants that have leaves that occur only on one side of the stem. Usually the leaves are held on a gently curved stem. This pattern is called monostichous. Spiral ginger (Costus) Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Alternate- single leaf per node Distichous leaves are arranged in two rows on opposite sides of the stem. Bald cypress (Taxodium) Back to main leaf menu Solomon’s seal (Polygonatum) Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Alternate- single leaf per node Traveler’s palm (Ravenala madagascariensis) has a spectacular distichous leaf form. Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Alternate- single leaf per node Several types of succulent plants display distichous leaves. Aloe plicatilis Back to main leaf menu Gasteria Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Opposite – two leaves per node Opposite is where a pair of leaves occur at each node. Subopposite is when some of the leaves are not perfectly paired but the distance between the nodes are not far enough apart to be considered alternate in arrangement. Wintercreeper (Euonymus) Honeysuckle (Lonicera) Subopposite Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Whorled – three or more leaves per node In the whorled arrangement, three or more leaves arising from the same node to form whorls of leaves along the stem. Horsetail (Equisetum) Back to main leaf menu Joe pye weed (Eupatorium) Back Next Lily (Lilium) Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Equitant Equitant leaves are overlapping as is typical in some Iris. Back to main leaf menu Back Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Decussate Decussate leaves are arranged opposite at each node, but each pair of leaves is oriented at right angles to the pair at the next node. Crassula perforata Back to main leaf menu Thujopsis dolobrata Back Next Mottlecah (Eucalyptus macrocarpa) Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Basal In a basal arrangement, all the leaves arise from the base (crown) of the plant. Spider plant (Chlorophytum) Back to main leaf menu Back Pineapple lily (Eucomis) Next Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu Leaf Arrangements Rosette Rosette leaves arranged in a dense, radiating cluster. Rosettes usually form near the base of the plant. Mosaic flower (Ludwigia sedioides) Back to main leaf menu Back Mullein (Verbascum) Back to vegetative parts main menu Main menu