* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Greece
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
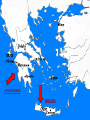
Greece – Classical Age Chapter 6-1 Geography of Ancient Greece Video: Minoans and Mycenaeans – 25m TN SPI – 6.5.11 1 Directions • For today’s lesson, you will need a sheet of notebook paper folded as a 4-square. • Colored Pencils Geography and Agriculture Trading Cultures Government City-States Geography of Ancient Greece • Greece is a country made up of: – Small scattered islands – Rugged mountains – Many peninsulas – Few valleys and coastal plains for farming – Isolated communities 4 5 Agriculture • Because of geography, farming was often difficult. • Good farmland was located by the coast and in the valleys. • Farms were usually small and only produced enough food to feed one family with a little extra to sell at the market. – Major crops: wheat, barley, olives, grapes – Farm animals: pigs, poultry, sheep, goats 6 Geographic Borders • Greece is bordered by: – – – – – Aegean Sea -East Ionian Sea - West Mediterranean Sea - South Macedonia – North Mt. Olympus – 9,570’ • Since travel inland across rugged mountains was so difficult, the early Greeks became skilled shipbuilders and sailors. • The sea was for travel, trading, and a source of food. 7 MACEDONIA TROY IONIAN SEA AEGEAN SEA OLYMPIA ATHENS SPARTA CRETE MEDITERRANEAN SEA 8 9 10 Trading Cultures • Two of the earliest cultures that settled in Greece were: – the Minoans – seafaring traders (non Greek) – the Mycenaeans – considered the first Greeks 11 The Minoans • The Minoans lived on the island of Crete located south of Greece in the Mediterranean Sea. • Although they lived in what is now Greece, they are not considered to be Greek because they didn’t speak the Greek language. • They were among the best shipbuilders and traders in the Mediterranean. – They traded pottery and olive oil for copper, gold, silver, and jewels. – A volcano erupted in the c1600 BC ending the Minoan civilization. 12 The Mycenaeans • The Mycenaeans were the first to speak the Greek language and are considered by historians to be the first Greeks. • They were builders of fortresses all over the Greek mainland and often attacked other kingdoms. • Historians believe the Mycenaeans attacked the city of Troy, possibly starting the legendary Trojan War. – The Mycenaean civilization was defeated by invaders from Europe in c1200 BC. – This period in Greek history is referred to as the Dark Age of Greece. 13 MYCENAEANS MINOANS 14 Greek City-States • Geography prevented small communities from coming together. For this reason small citystates (a city and the surrounding area) formed which had their own: – Traditions – Governments – Laws – Leaders • Hundreds of Greek city-states formed. Athens, Sparta, Olympia, and Troy were most well known. 15 Life in City-States • Life in the city often focused on the marketplace, or agora. • Many shops bordered the agora. • Farmers brought their crops to the market to trade for goods made by artisans. • The agora was a large open space that also served as a meeting place for political and religious meetings. 16 Government - Who Ruled? • Oligarchy – rule by a small group (Sparta) – Early Greeks were governed by aristocrats, or a small group of rich landowners. – As trade increased, a middle class began to grow who resented the aristocracy. – The middle class demanded a role in government. 17 Government - Who Ruled? • Direct Democracy – citizens govern themselves (no elected representatives) – Athens formed a democracy . – Must be a male citizen 18 years of age. – Both parents must be Athenian to be considered a citizen. – Women were not allowed to debate laws. 18 Democracy Then and Now Direct Democracy • All citizens met as a group to debate and vote on every issue. • There was no separation of powers. Citizens created laws, enforced laws, and acted as judges. • Only free male citizens could vote. Women and slaves could not vote. Republic - Indirect Democracy • Citizens elect representatives to debate and vote on issues for them. • There is a separation of powers. Citizens elect people to create laws, others to enforce laws, and others to be judges. • Men and women who are citizens have the right to vote. 19