* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lower Limb 3: Gluteal Region
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
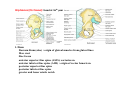
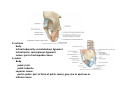
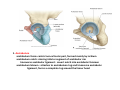
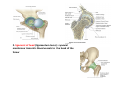
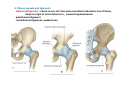
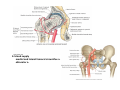
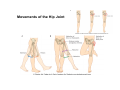
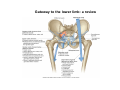
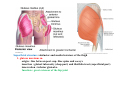
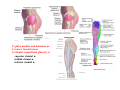
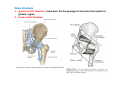
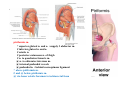
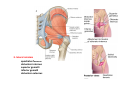
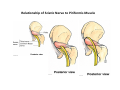
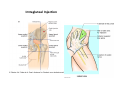
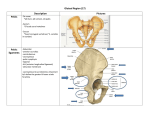
歐陽品教 授 12/01/2015 Lower Limb 3: Gluteal Region Gluteal region: posterior to the pelvis and inferior to the level of the iliac crest Surface anatomy line between 2 iliac crests-----L4 line between 2 post. Sup. Iliac spines -----S2 tip of coccyx------- level with greater trochenter ischial tuberosity------at level with lesser trochanter Hip bones (Os Coxae): fused at 16th year 1. Ilium Dorsum ilium (alae) : origin of gluteal muscles from gluteal lines Iliac crest iliac fosssa anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS): sartorius m. anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) : origin of rectus femoris m. posterior superior iliac spine posterior inferior iliac spine greater and lesser sciatic notch 2. ischium body ischial tuberosity: sacrotubulous ligament ischial spine: sacrospinous ligament ramus: part of ischiopubic ramus 3. pubis Body pubic crest pubic tubercle superior ramus pectin pubis: part of brim of pelvis minor, give rise to pectinus m. inferior ramus 1. Acetabulum acetabulum fossa: central non‐articular part, formed mainly by ischium acetabulum notch: missing inferior segment of acetabular rim transverse acetabular ligament : covert notch into acetabular foramen acetabulum labrum : attaches to acetabulum ring and transcerse acetabular ligament, forms a complete ring around the femur head 2. ligament of head (ligamentum teres) : synovial membrane transmits blood vessels to the head of the femur 3. fibrous capsule and ligaments iliofemoral ligament : attach to ant. Inf. Iliac spine and intertrochanteric line of femur, deep to origin of rectus femoris m., prevent hyperextension pubofemoral ligament ischiofemoral ligament: weakest one 4. blood supply medial and lateral femoral circumflex a. obturator a. Movements of the Hip Joint Gateway to the lower limb: a review Superficial structure: abductor and medial rotators of the thigh 1. gluteus maximus m. origin : line between post. sup. iliac spine and coccyx insertion : gluteal tuberosity (deep part) and iliotibila tract (superficial part) innervation : inferior gluteal n. function : great extensor of the hip joint 2. glutei medius and minimus m. 3. tensor fascia lata m. 4. Clunial (superficial gluteal ) n. superior clunial n. middle clunial n. inferior clunial n. Deep structure 1. greater sciatic foramen : main door for the passage of structure from pelvis to gluteal region 2. lesser sciatic foramen piriformis m. * superior gluteal n. and a. : supply 3 abductor m. # inferior gluteal n. and a. # sciatic n. # posterior cutaneous n. of thigh # n. to quadratus femoris m. @ n. to obturator internus m. @ internal pudendal vessels @ pudendal n. : behind sacrospinous ligament * above piriformis m. # and @ below piriformis m. @ via lesser sciatic foramen to ischiorectal fossa 3. lateral rotators quadratus femoris obturator internus superior gemelli inferior gemelli obturator externus Relationship of Sciatic Nerve to Piriformis Muscle Intragluteal Injection