* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download gluteal complex
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
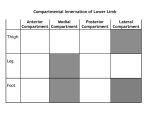
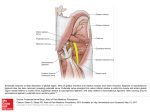
GLUTEAL COMPLEX Bony Landmarks Ligaments of articulated pelvis: Obturator membrane. Sacrotuberous: Posterior iliac spine, lower sacrum, coccyx to ischial tuberosity. Sacrospinous: Sacrum, coccyx to ischial spine. Greater sciatic foramen. Lesser sciatic foramen. Sacroiliac. Iliolumbar. Sciatic Foramina Greater sciatic foramen: Piriformis muscle. Sciatic nerve. Superior/inferior gluteal vessels and nerves. Pudendal nerve. Internal pudendal artery/vein. Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. Nerves to quadratus femoris and obturator internus. Sciatic Foramina Lesser sciatic foramen: Tendon of obturator internus. Nerve to obturator internus. Pudendal nerve. Internal pudendal vessels. Cutaneous Innervation Upper medial quadrant: Posterior rami of L1-3, S1-3. Upper lateral quadrant: Iliohypogastric nerve (L1) Anterior rami T12. Cutaneous Innervation Lower medial quadrant: Branches from posterior femoral nerves (S1-3) Lower lateral quadrant: Branches from lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (S2-3). Muscles Posterior gluteal compartment: Muscles: Gluteus maximus. Innervation: Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1-2). Vascular supply: Inferior gluteal artery: From internal iliac. Muscles Posterior gluteal compartment: Action: Hip extension and lateral rotation. Rising, climbing, running (but not walking). Muscles Lateral gluteal compartment: Muscles: Gluteus medius. Gluteus minimus. Medius and minimus are the same muscle separated by the superior gluteal nerve. Tensor fascia latae: Inserts onto iliotibial tract. Muscles Lateral gluteal compartment: Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve. Vascular supply: Superior gluteal artery: From internal iliac. Action: Hip abduction with a free-swinging limb. Muscles Trendelenburg test: Evaluates strength of contralateral gluteus medius. Patient stands upright and raises one foot off the ground. Contralateral gluteus medius should lower contralateral hip and raise ipsilateral hip. Needed to clear foot from the ground during swing phase of walking. Muscles Six deep external Piriformis: rotators: Leaves pelvis through greater sciatic foramen. (Main door for passage of structures from pelvis to thigh.) Superior gemellus. Obturator internus. Inferior gemellus. Obturator externus. Quadratus femoris. Vascular Supply Internal iliac artery: Arises from common iliac artery. Branches: Superior gluteal. Inferior gluteal. Vascular Supply Internal iliac artery: Branches from femoral artery: Medial femoral circumflex artery: Ascending branch anastomoses with inferior gluteal artery. Lateral femoral circumflex artery: Ascending branch anastomoses with superior gluteal artery. Bursae Trochanteric. Gluteofemoral. Ischial (sciatic).