* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2010 4 13_Back to basics neonatology for 4th yr MS_Part 4 2010
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of syphilis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
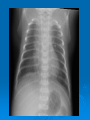
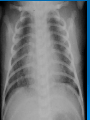
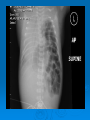
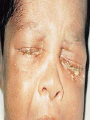
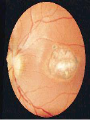
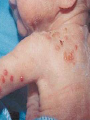
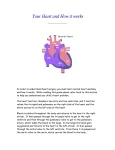
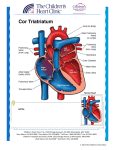
Postmaturity Labour tends to be induced to avoid problems of postmaturity, however if dates not accurate may still occur Possible complications Growth disturbances Asphyxia Meconium aspiration syndrome Problems of the Term Newborn Respiratory Cardiac Sepsis Digestive Jaundice Anemia, polycythemia, hemorrhage Renal Endocrine Neurologic Respiratory Distress in the Newborn Respiratory Cardiac Infectious Neurologic Metabolic Gastrointestinal Hematological Musculoskeletal Respiratory Problems in the Term Newborn Transient tachypnea of the newborn Pneumonia Meconium aspiration Pulmonary air leaks Congenital malformations Persistent pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary hemorrhage Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn Failure to clear lung fluid Associated with: Absent labour (planned C/S or C/S without labour) or; Short labour or; Initial weak or absent respirations Improves with time Pneumonia Can initially be difficult to distinguish from TTN/RDS Group B Strep #1 Consolidation days may appear after a few Meconium Aspiration Syndrome Meconium-stained amniotic fluid Intrauterine insult may lead to gasping Meconium aspirated Pneumonitis Airway occlusion Pulmonary air leak syndrome May lead to persistent pulmonary hypertension Congenital Malformations Anomalies anywhere along airways: Nose to alveoli Extrinsic or intrinsic Atresias Cysts Diaphragmatic hernia Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with: Asphyxia Meconium aspiration Sepsis Right to left shunting through PDA (i.e. persistent fetal circulation) Treatment: Oxygenation, ventilation Maintain blood pressure Pulmonary vasodilators Congenital Heart Disease: Presentations Cyanosis Congestive heart failure Murmurs Dysrhytmias Sepsis: Risk factors Preterm rupture of membranes e.g. weeks Prolonged rupture of membranes >18 hours Maternal group B strep carriage Maternal GBS bacteriuria Previous infant with GBS infection Chorioamnionitis Neonatal Sepsis THINK OF IT! Signs may be subtle, non-specific Incidence bacterial sepsis = 1-5/1000 live births Commonest organisms: • Group B streptococcus • Gram negatives (E coli, Klebsiella) • Enterococcus, H flu, staph species • Listeria Work up and treat if suspect sepsis Use broad spectrum antibiotics Ophthalmia neonatorum 1st days - differentiate chemical vs infected 2nd-3rd wk - viral or bacterial Gonococcal: within 5 days of birth gram negative intracellular diplococci if suspect, Penicillin asap highly contagious Chlamydia: 5-14 days conjunctival scraping topical antibiotics Congenital Infections CMV: 5-25/1,000 live births Asymptomatic vs severe symptoms Microcephaly, thrombocytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, chorioretinitis Sequelae of hearing loss and developmental delay Rubella 0.5/1,000 Cataracts, rash, congenital heart disease, developmental delay Congenital Infections Toxoplasmosis: 0.5-1.0/1,000 Hydrocephalus, cranial calcifications, chorioretinitis Syphilis: 0.1/1,000 Snuffles, osteochondritis/periostitis, rash Herpes Simplex Virus: Vesicles, keratoconjuntivitis, CNS findings ‘Viral’ sepsis Congenital syphilis Treat mother no matter what stage of pregnancy If adequate maternal treatment and no signs of infection in newborn, give one dose IM penicillin If inadequate maternal treatment, give 10 days of IV penicillin Neonatal herpes simplex Only about 1/3 mothers have overt signs Infection Usually If can be disseminated or local present at 5-10 days of age suspect: Cultures, PCR Treat with Acylovir Maternal hepatitis B carrier Give baby hepatitis vaccine as soon as possible after birth (first 12 hours) Bath Universal Immune precautions globulin in first 7 days Virus HIV can be transmitted transplacentally, intrapartum, or postpartum Screen mothers Treat mothers with antiretrovirals Treat babies with AZT for 6 wks Universal precautions Look for other infections (HepB/C) No breastfeeding in developed world