* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FACTORS AFFECTING WEATHERING RATES
Survey
Document related concepts
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
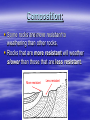
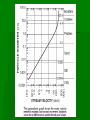
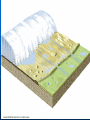
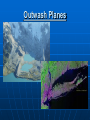
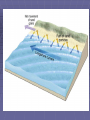
b TOPIC 9 WEATHERING & EROSION Weathering Vs. The breakdown of rock material Erosion The transport of broken down rock material Weathering Physical Breakdown of rock material without changing the chemical makeup of the rock. Example: smashing chalk with hammer. Chemical Breakdown of rock material by changing the chemical makeup of the rock Example: dissolving chalk in acid Frost Action- water expands when frozen Plant Action Abrasion Oxidation Carbonation Hydration Cape May “Diamonds” FACTORS AFFECTING WEATHERING RATES Particle Size Composition of Rock Climate Exposure Particle size: rate As particle size increases, weathering rate decreases. (indirect relationship) This is due to an increase in surface area. size Composition: Some rocks are more resistant to weathering than other rocks. Rocks that are more resistant will weather slower than those that are less resistant. More resistant Less resistant You might also see it like this… Climate: Warm climates - Chemical weathering Cold climates - Physical weathering As moisture increases, weathering rates increase or… “Wetter is Better !!!” a warm, moist climate will have greater weathering rates than a warm, dry climate Cleopatra’s Needle Exposure: As a rocks exposure to the Earth’s surface increases, the weathering rate increases. Im OK! EROSION: *GRAVITY is the driving force behind erosion ! The 5 Agents of erosion are… Streams Glaciers Wind Waves Gravity Stream Erosion The most predominant agent of erosion. Why? Methods of transport: Stream velocity depends on… Gradient (slope) -as slope increases, velocity increases. Discharge (amt. of water in the stream) -as discharge increases, velocity increases. Velocity vs. Sediment When the velocity increases… 1. The amt. of sediments carried increases 2. The size of the sediments carried increases. Erosion Frost action Oxidation Caves Abrasion Plant action Hydration Weathering Discharge Meander Delta Alluvial fan Horizontal sorting Streams move fastest… Just below the surface In the center of the channel Meanders High KE More Erosion Low KE Less Erosion * Water moves fastest on the outside of meanders. DELTA: Sediments deposited at the mouth of a stream. Sediments are deposited because the stream velocity decreases abruptly. Horizontal Sorting The sediment size decreases as the distance from the mouth increases. Largest Sediments Smallest sediments Alluvial Fan (land delta) Fan shaped deposit formed when streams flow off of mountains onto more level land. Stages of Stream Development Stream Sediments Sediments deposited by a stream are usually sorted, rounded and smooth. Narrow V-shaped Downcutting Swift water Steep gradient Erosion is dominant Wide meanders and oxbow lakes Wide floodplain Low velocity Low gradient Dynamic equilibrium between erosion and deposition Glaciers Large mass of moving ice. Continental vs. Mountain glaciers. Ice forms from the pressure caused by the weight of the accumulating snow. Glacial features: Till- sediments transported by glaciers Sediments are Unsorted and Angular. Glacial features: Till- sediments transported by glaciers Sediments are Unsorted and Angular. Striations- scratches and grooves in bedrock. Glacial features: Till- sediments transported by glaciers Sediments are Unsorted and Angular. Striations- scratches and grooves in bedrock. Erratics-large boulders deposited by a glacier that DO NOT match the local bedrock. U- Shaped Valleys Stream Valley Glacial Valley Moraines Other Features: Drumlins Other Features: Drumlins Eskers Long Island- Terminal Moraine Long Island- Terminal Moraine Finger Lakes Other Features: Drumlins Eskers Kames Long Island Finger Lakes Crevasses Valley Glacier Continental Glacier Till Erratics Striations Drumlins Eskers Kettles Kames Outwash Planes Outwash Moraine WIND EROSION Wind transported sediments are… 1. Small 2. Dry 3. Loose (free to move) ** Sediments are frosted and pitted Features: Wind erosion may cause abrasion. ex: Arches, toadstools, ventifacts, desert pavement Deflation Sandblasting Winds blow sand against rocks causing abrasion. Dune: Deposit of windblown sand. WAVE EROSION Sediments are transported due to the energy created by breaking waves. Mass Movement: Any variety of erosion and/or deposition done directly by gravity. Examples: Rock slides Avalanches Slump Creep Deposits are unsorted and angular. Mr. Arcuri John Deere Cafeteria Mr. Egresits Stewarts Golden Knights Mr. Andrews Mr. Goodelle