* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
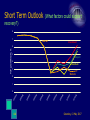
Economic and financial challenges: prospects of Albania. Ardian Fullani Governor of Bank of Albania Athens October 2009 Preview 2 Policy Framework & Long run Quest for Stability Addressing domestic external vulnerabilities Crisis hits region Channels of transmission Economic impact Short term outlook Long run implications Saturday, 13 May 2017 Policy Framework Inflation is the final objective From Monetary targeting (intermediate targets: M3) to Implicit inflation targeting (Two pillar strategy with leading indicators: Forecasted inflation and M3 growth) Open Market operations Weekly Repo. Rate Reserve requirements Free floating exchange rate. 3 Exchange rate acts as shock absorber. Saturday, 13 May 2017 Long Run Quest for Stability Emphasize and focus on long run sustainable equilibrium: Prudent monetary policy, aiming to preserve macroeconomic stability and promote savings in the economy. Free floating exchange rate. Encourage fiscal consolidation and policy coordination (Fiscal Rule). Approve New Banking Law and Repurchase Agreement Law and the respective regulatory framework. Establish a continuous dialogue with the market participants. Improve commercial bank governance, transparency and internal control and Better risk management. Warn banks and take regulatory measures against fast credit growth, especially in foreign currency. 4 Saturday, 13 May 2017 Vulnerabilities Before Crisis Consumption led growth due to fast credit expansion. Increasing fiscal deficits. Growing trade and current account deficits. 5 EU main trade partner. Saturday, 13 May 2017 Crisis: Channels of Transmission and Economic Impact Foreign and domestic demand slows. Remittances slow. Deposit withdrawals. Liquidity problems for banks. Credit stops; Private investments & consumption suffers. Exchange rate depreciates. Agents realize the problem of borrowing in foreign currency. Commodity prices drop prevents automatic adjustment of CAB. 6 Depreciation is not passed to prices and inflation stays within the Bank of Albania objective. Saturday, 13 May 2017 Crisis: Policy Response Bank of Albania January 2009 Repo Rate cut 50bps; Provide all needed liquidity in domestic currency; Contain exchange rate volatility and agents emotional response to market fluctuations; Increase efficiency and Micro management in the foreign exchange market; Downward economic forecasts for economic activity; Share information with other supervisory authorities aiming to coordinate and customize policy response in line specific market conditions. Fiscal Increase capital expenditure 7 Privatization and foreign commercial borrowing; Aggressive borrowing in domestic markets with signs of crowding out. Saturday, 13 May 2017 Crisis: Policy Response Shift focus toward financial stability Open market operations: Change the form of Repo auctions from fixed amount to fixed price; Extend the average maturity of Central Bank liquidity injection; Reduce the margin of overnight lending from + 175 bps to + 75 bps; Expand the range of collateral: from TBiIls with up to 1 year maturity to securities with days to maturity up to one year; Increase the daily use of the required reserve from 20 to 40 percent. Exchange rate interventions: Reduce extreme exchange rate volatility and other market imperfections, while domestic agents adjust to new equilibrium. Encourage banks to credit the economy. 8 Saturday, 13 May 2017 Policy Response and Economic Impact Inflation stays low. Aggregate demand slows down; Deflation in the commodities prices offsets the FX depreciation on inflation. Government deficit grows. Yield curve Steppes with possible crowding out effects. 9 Saturday, 13 May 2017 Short Term Outlook (Growth prospects) 8 7 INSTAT 5 4 September 3 2 June 1 May 10 20 10 Q 2 20 10 Q 1 20 09 Q 4 20 09 Q 3 20 09 Q 2 20 09 Q 1 20 08 Q 4 20 08 Q 3 20 08 Q 2 0 20 08 Q 1 YoY growth rate, % 6 Saturday, 13 May 2017 Short Term Outlook (What factors could support recovery?) 8 7 INSTAT Investment 5 Export s Euro/Lek 4 3 Outlook 2 1 11 20 10 Q2 20 10 Q1 20 09 Q4 20 09 Q3 20 09 Q2 20 09 Q1 20 08 Q4 20 08 Q3 20 08 Q2 0 20 08 Q1 YoY growth rate, % 6 Saturday, 13 May 2017 Long Run Implications: Possible Structural Effects Monetary policy Fiscal policy Slower growth in M3 due to reduced velocity (less credit in foreign currency). Less credit demand due to portfolio rebalancing and bank tougher standards. Larger and persistent fiscal deficits. Difficult refinancing. Emergence of twin deficits. Financial Stability Rebalance of saving & consumption behavior in favor of domestic currency. 12 Saturday, 13 May 2017 Long Run Policy Implications Structural shifts (Unit root vs. mean reverting) in: Structure of credit Structure of money World GDP growth Monetary policy implications of future developments in GDP, and money supply Implications for transmission mechanism and monetary policy reformulation (monetary indicators). Structural reforms needed in several areas. 13 Saturday, 13 May 2017