* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download High Voltage Batteries
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electric vehicle wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
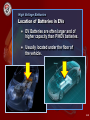
NFPA ELECTRIC VEHICLE SAFETY FOR EMERGENCY RESPONDERS Module III: Vehicle Systems and Safety Features 3-1 NFPA ELECTRIC VEHICLE SAFETY FOR EMERGENCY RESPONDERS Module III: Vehicle Systems and SafetyFeatures Module III Objectives Terminal Objective Describe the operation of P/HEV and EV systems. Enabling Objectives ● ● ● ● Define terms related to P/HEV and EV systems. Compare and contrast P/HEV’s and EV’s. List major components of P/HEV systems. List major components of EV systems. 3-2 Hybrid Electric (HEV) All hybrids use batteries and electric motors to reduce demand on the internal combustion engine (ICE). ● Allows better fuel economy. Toyota Prius ● ICE can shut down when not needed. ● Some Hybrids can drive short distances on electric power only (silent movement hazard). ● For response purposes, treat all hybrids the same. Honda Civic Hybrid 3-3 Plug-In Hybrid Electric (PHEV) A hybrid vehicle that allows the battery to be charged via an external power source. • Increases battery charge • Increases range • Reduces dependence on the gasoline engine. 2012 Toyota Prius 3-4 Electric Vehicle • • Electric motors are the only means of propulsion. Vehicle must be charged by an external power source. Nissan Leaf 3-5 Extended Range Electric Vehicle • Electric motors provide the propulsion. • When battery is low, gasoline generator provides the electricity for the motor. • Chevrolet Volt For emergency response, treat as a PHEV with… • • • • a gasoline engine high voltage battery electric propulsion possible external power. 3-6 High Voltage Battery Recharging 3 Methods Engine Power Regenerative Braking External Power (Plug In) 3-7 Term: Regenerative Braking ● During braking, wheels turn the electric motor, making it act as a generator and produce electricity. ● Electricity routed to HV battery to increase charge. Can damage HV system if towed with drive wheels on ground (fire hazard). 3-8 Video Vehicle Types 3-9 Video Vehicle Types 3-10 Response Breakdown Vehicle types by hazards High Voltage and Fuel ● Hybrids ● Plug-in Hybrids ● Extended Range EVs High Voltage Only ● Pure EVs 3-11 HEV / PHEV / EV VEHICLE COMPONENTS 3-12 Standard Components Internal Combustion Engine (Not in EVs) 12 Volt DC Battery 12 VDC battery can be located in various locations around vehicle. Common Locations: · Trunk / Cargo compartment · Under hood Less Common Locations: · Front wheel well · Under 2nd Row seats 3-13 High Voltage Batteries Battery Types NiMH Lithium Ion Nickel Metal Hydride Various Materials 3-14 High Voltage Batteries Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery ● Most common battery in HEVs. ● Electrolyte is caustic alkaline and may produce harmful fumes if exposed. 3-15 High Voltage Batteries Lithium Ion (Li-Ion) Battery ● Most common in PHEVs and EVs. ● Different from Li-Ion batteries in home electronics. ● Electrolyte may produce harmful, flammable fumes if exposed. 3-16 High Voltage Batteries Small Cells in Series ● High voltage batteries are made of many small, lowvoltage cells. ● Small cells wired in series to multiply voltage. ● Ex: Four 1.5 VDC batteries in series equals 6 VDC. 3-17 High Voltage Batteries Location of Batteries in HEVs, PHEVs Generally located in rear of vehicle. Under 2nd row seating in most SUVs and trucks, in trunk/ cargo area in most sedans. 3-18 High Voltage Batteries Location of Batteries in EVs ● EV Batteries are often larger and of higher capacity than P/HEV batteries. ● Usually located under the floor of the vehicle. 3-19 Video 12 VDC and High Voltage Batteries 3-20 Video 12 VDC and High Voltage Batteries 3-21 High Voltage Batteries Service Disconnects ● Recommendations for use and required safety equipment vary by manufacturer. Consult appropriate ERG before using service disconnect. ● Located on the HV battery. ● Physically disconnects the HV battery from HV systems. Service disconnect will be addressed later in course. 3-22 Inverter/ Converter Located under hood ● Found in vehicles using AC drive motors. ● Converts DC from HV Battery to AC to run motor. ● Converts AC from regenerative braking back to DC to charge HV Battery. 3-23 Inverter/ Converter Located under hood Dangerous to penetrate cover with tools. ● Capacitors inside unit can store energy for a period of time. ● If damaged, capable of rapid energy discharge that can cause severe injuries. 3-24 DC-DC Converter ● Serves as second 12V power supply (in addition to 12V battery). DC-DC Converter (APM) for Chevrolet Volt ● Provides same functions as alternator in conventional vehicles. ● Steps down high voltage DC from the HV battery to 12 VDC to run low voltage systems. 3-25 DC-DC Converter ● In some models the DC-DC converter is housed in the inverter/converter module. 3-26 High Voltage Battery Relay ● Located on HV Battery. ● Functions like a switch. ● Activated by 12v power from the low voltage system ● Removal of 12v power causes the relay to open, stopping the flow of HV current 3-27 Video The 12V System and the HV Relay 3-28 Video The 12V System and the HV Relay 3-29 Video High Voltage Battery Relay Animation 3-30 Video High Voltage Battery Relay Animation 3-31 EV/ HEV Cabling Color coded to SAE voltage levels ● Low Voltage: <30 Volts Often Red or Black ● Intermediate: 30-60 Volts Usually Yellow or Blue ● High Voltage: >60 Volts Orange 3-32 Medium/High Voltage Cabling Medium and high voltage should both be considered highly dangerous. For safety, treat yellow and blue cables the same as high voltage orange. 3-33 High Voltage Cabling Location ● Between the HV battery, HV components, and the electric motor. ● Typically routed along the underside of the vehicle and under hood. 3-34 High Voltage Cabling Construction/Fault Protection If a cable is compromised or damaged, the system is designed to detect the damage and shut down. For safety, ALL high voltage cable should be considered energized during response operations. 3-35 Electric Motors • Provide propulsion in EVs and some P/HEVs. • Start and stop the ICE when not needed. • Recharge HV battery through regenerative braking and ICE. • Sometimes called Drive Motors or Traction Motors 3-36 Safety Systems P/HEVs and EVs have safety systems designed to automatically shut down the high voltage systems in the event of: ● Crash Impact ● Airbag Deployment ● Cabling Damage ● Short Circuits However, always treat HV systems as energized for maximum safety. 3-37 Charging Ports • Connects charging cord to vehicle. • Charging components reside on the vehicle. • The charging unit is an interface between the power supply and the vehicle. 3-38 Charging Stations Level I Level II 120 VAC 8-16 hours 240 VAC 3-8 hours DC Quick Charge 480 VDC 20-30 min. 3-39 Level 1 Charging Station Level I 120 VAC 8-16 hours ● Utilizes 120VAC power. ● Uses standard household plug. ● Slowest rate of the three levels. ● Can accompany vehicle to charge it anywhere. 3-40 Level II Charging Station Level II 240 VAC 3-8 hours ● Utilizes 240VAC power. ● Can be a fixed installation or portable unit. ● Faster than Level I systems. Typically 3-8 hours depending on the size of the battery. 3-41 J1772 Plug and Receptacle ● SAE standardized for Level I and II charging. ● Multi-pin charging/ communication link between charger and vehicle. ● Conducts current. ● Relays charge status. ● Shuts down charging when battery “full.” ● Prevents vehicle from moving when pluggedin. 3-42 DC Quick Charge Station DC Quick Charge ● Currently provides 480VDC directly to the battery. 480 VDC 20-30 min. ● New standards being developed, so this may change. ● Fastest charging system. ● Due to wiring requirements, availability, and expense, will likely be in commercial sites only. 3-43 Charging Stations 3-44 Charging Stations 3-45 Activity 3.1 P/HEV, EV Components You will be shown a series of slides, each with a picture of a component of a P/HEV or EV. You will be given a few moments to discuss and decide on the name of the component and its function. Be prepared to share your answer with the class. 3-46 ? 3-47 Component High Voltage Battery Function The electrical storage system that provides power for vehicle systems. 3-48 ? 3-49 Component High Voltage Cabling Function Wiring used to carry electric current from the high voltage battery to the electrical motor. 3-50 ? 3-51 Component Inverter / Converter Function Devices which convert DC from the high voltage battery to AC to drive the motor. 3-52 ? 3-53 Component Charging Ports Function Electrical connections on a vehicle for connecting the high voltage battery to a charging source. 3-54 ? 3-55 Component Manual Service Disconnect Function Cuts off the battery from the high voltage system. Refer to Manufacturer ERG before use! 3-56 ? 3-57 Component J1772 Connector Function Multi-pin communication link between charger and vehicle. 3-58 Module Summary 3- • There are several different types of P/HEVs and EVs. • Each one has specific components related to its electrical identify. • Familiarity with the types, components and differences will facilitate emergency operations. 59 3-59