* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion of Buddhism
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and violence wikipedia , lookup
Buddha-nature wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist influences on print technology wikipedia , lookup
Pratītyasamutpāda wikipedia , lookup
Persecution of Buddhists wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist texts wikipedia , lookup
Dhyāna in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Tara (Buddhism) wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist art wikipedia , lookup
Early Buddhist schools wikipedia , lookup
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Nirvana (Buddhism) wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Sanghamitta wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Korean Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Dalit Buddhist movement wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Thailand wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in Cambodia wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
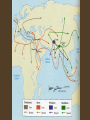
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Diffusion of Buddhism Answer the following question in a complete paragraph • Is there such thing as a “pure” version of a religion? Should a religion be unchanging to provide an anchor-point or should it adapt and change with the times to remain relevant? Origins • Siddhartha Guatama was a kshatriyacaste prince in the NE of India. • After attaining nirvana, he lived decades during which he wandered and preached • By preaching he set in motion the “Wheel of Dharma” (or “Wheel of Law”) • Buddhism appealed mainly to the lower castes of India and those outside the control of the Hindu heartland Initial Spread • Mauryan emperor ASHOKA converted to Buddhism and ruled according to Buddhist principles • The Edicts of Ashoka were written law • Ashoka encouraged missionary activity – esp. to Sri Lanka (Ceylon) Ashokan Pillar Syncretic Buddhism • Buddhism was originally an individualistic,, psycho-spiritual discipline with no gods, church, or rituals • As it spread, it became more like a religion: – The Buddha became god-like – Stupas (shrines) were erected over remains of the Buddha; pilgrimages to the shrines became important – Monasteries with hierarchies of monks and nuns stared – Local gods and goddesses were absorbed as Bodhisattvas Tibetan Stupa Mahayana Buddhism • The “greater vehicle”: Buddhism for the masses • Theistic and syncretic • Key role of Bodhisattvas Kuan yin East Asian White Tara Tibetan Theravada (Hinayana) Buddhism • • • • • • “Traditional” Buddhism Non-theistic Individualistic Anti-ritualistic “pure” Hard for most people to understand Buddhism spread North, East, and SE • Spread into Himalayas – Tibetan Buddhism • Spread along Silk Road to China: – “Pure Land” Buddhism (Salvationist) – Chen Buddhism (“awareness “ Buddhism) Spread of Buddhism • Chen Buddhism spread through Korea into Japan, where it was blended with SHINTO (nature religion) and became ZEN Spread of Buddhism • Spread through IO network into SE Asia – Sometimes Mahayana (syncretic) e.g. Indonesians – Sometimes Therevada, e.g. Thai, Burmese Buddhism back in India • New developments in Hinduism and the perceived difficulty of Theravada caused two reactions: – Syncretic Buddhism (Mahayana) – Retreat of Buddhism Buddhism became a minority religion in India after Ashoka