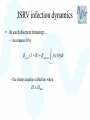* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OPA_modelling_progress
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
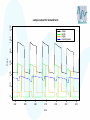
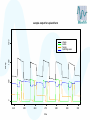
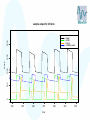
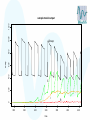
Modelling – progress update Stephen Catterall, BioSS 28th November 2007 Contents • Sheep flock model – Refinements • JSRV infection model – Progression to clinical disease – Transmission • Conclusion Sheep flock model • • • • Status: it has now been implemented in ‘C’ Very fast! Three versions: hill, upland, lowland Refinements: – Lamb mortality modelling – Incorporate variability between farms 1200 sample output for lowland farm 600 400 200 0 sheep 800 1000 sheep lambs hoggs breeding ewes 240 250 260 270 time 280 290 300 500 1000 sheep lambs hoggs breeding ewes 0 sheep 1500 sample output for upland farm 240 250 260 270 time 280 290 300 sample output for hill farm 1000 500 0 sheep 1500 2000 sheep lambs hoggs breeding ewes 240 250 260 270 time 280 290 300 JSRV infection dynamics • Status: the JSRV infection model has been implemented in ‘C’ • However, more data is needed so as to better estimate some of the parameters • Assume: – – – – All sheep initially susceptible Some sheep acquire infection (without being infectious) At some point later on, the sheep becomes infectious After some time the sheep then develops clinical symptoms JSRV infection dynamics S Not infected E Infected Not infectious Not clinical STANDARD MORTALITY voluntary/involuntary culling I Infected Infectious Not clinical CLINICAL removal from flock JSRV infection dynamics • Modes of transmission – Horizontal transmission – Vertical transmission? close contact between the ewe and her lamb – Indirect transmission via the environment?? not very important but cannot be excluded? • All three modes of transmission have been implemented within the model JSRV infection dynamics • Simulation of transmission… – When initialising a susceptible sheep, take U from U (0,1) – and compute H max ln U – set H=0 JSRV infection dynamics • At each discrete timestep… – Increment H by direct ( I R) indirect tn f (c(t ))dt t n 1 – the sheep acquires infection when H H max 1000 1200 sample model output 600 400 200 E I R 0 sheep 800 Sheep 300 320 340 360 time 380 400 420 In summary • Sheep flock model – Complete subject to a few refinements – A paper describing the model is being written • JSRV infection transmission model – This has been implemented in ‘C’ – Three modes of transmission modelled – ‘Estimation’ of key parameters is still required