* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Knight`s Definition A force
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
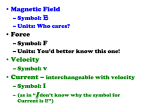
Force Types Definition of Force Drawing the Force Dimensions and Units of Force Tension Elastic Force Gravity Normal Force Friction Drag Pulleys 1 Force Types Force That which causes a particle to accelerate. It is a vector! Knight’s Definition A force … is a push or a pull on an object. It is a vector. It has both magnitude and direction. It requires an agent. Something does the pushing or pulling. It is either a contact force or a long-range force (gravity). 2 Force Types Force, like any vector is drawn as an arrow with the symbol or magnitude and units. The tail of the force is placed on the part of the object that is experiencing the force. In a free-body diagram, the tail is placed on the point representing the particle. The direction of the force and its magnitude are determined by the type of force it is. 3 Force Types Force The SI unit of force is the Newton (abbreviated as N). One Newton is the same as one kilogram-meter per second squared. Another unit of force is the pound. 4 Force Types Tension T The magnitude of the tension is the same everywhere in the rope. T 5 Force Types Name of Force Symbol 6 Tension T When does this force occur? If an object that is experiencing the force is pulling but not stretching another object Where does this force occur? On the object that is experiencing the force at the point where the pulling occurs Associated Energy No associated energy Force Types Spring Force k x Fsp 7 Force Types Name of Force Symbol 8 Spring Force Fspring When does this force occur? If an object that is experiencing the force is stretching (or compressing) another object Where does this force occur? On the object experiencing the force where it connects to the object that stretches/compresses Associated Energy Elastic Potential Energy Force Types Gravity m1 FG m2 r FG 9 Force Types Name of Force Symbol 10 Gravity FG or w When does this force occur? If there are two massive objects present Where does this force occur? At the center-of-mass of the object receiving the force Associated Energy Gravitational Potential Energy Force Types Normal Force N w 11 Force Types Name of Force Symbol 12 Normal Force n, FN or N When does this force occur? If an object touches the surface of another object Where does this force occur? On the object receiving the force at the point(s) where it touches the surface Associated Energy No associated energy Force Types Friction N f 13 Force Types Name of Force Symbol 14 Friction fs or fk When does this force occur? If an object touches the surface of another object Where does this force occur? On the object receiving the force at the point(s) where it touches the surface Associated Energy Thermal Energy Force Types Drag D 15 Force Types Name of Force Symbol 16 Drag D When does this force occur? If an object is moving through a liquid or gas. Where does this force occur? On the object receiving the force at the point(s) where it touches the liquid or gas Associated Energy Thermal Energy Force Types Pulleys Pulleys simply change the DIRECTION of a force. T T 17