* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Kingdom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
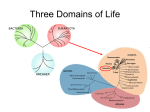
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS Far more diverse than Kingdom Plantae Consist of the most complex organisms consisting of about 2 million species Heterotrophic, multicellular eukaryotes belongs to this kingdom Vary in size – ranging from microscopic to the most gigantic creatures Kingdom Animalia are divided into 2 groups 1. Vertebrates - animals with backbones 2. Invertebrates - animal without backbone VERTEBRATES 1. MAMMALS - covered with hair and they have mammary glands - these gland secrete milk of females who have just delivered their young - warm-blooded animals Ex. Cats, dogs, goat, whales and dolphins MAMMALS VERTEBRATES 2. BIRDS -feathers cover their body - they have beaks or bill which they used to get food - they have a pair of wings that enable them to fly - they are also warm blooded animals that lay eggs from which their young is hatched BIRDS VERTEBRATES 3. REPTILES -they have thick, dry scales that cover the bodies of reptiles to prevent the excessive loss of water - they are cold blooded animals - some have four legs, while others have no legs at all REPTILES VERTEBRATES 4. AMPHIBIANS - live in water during the early stage of their life and begin to stay on land where they can get enough food - body is covered by a thin, flexible and usually moist skin - their eggs are fertilized externally AMPHIBIANS VERTEBRATES 5. FISH - they have scales as body covering and they breathe through the gills - they also have lungs for breathing - red snappers are all bony fishes - sharks and rays are cartilagenous fishes FISHES INVERTEBRATES 1. PHYLUM ECHINODERMATA - marine organisms with spiny skins - from the Greek terms echinos (meaning hedgehog) and derma (meaning skin) - the tube feet and system of canals in the body that serves as a channel for sucking in the sea water to obtain nutrients and for vomiting sea water ECHINODERMS ECHINODERMS INVERTEBRATES 2. PHYLUM ARTHOPODA - they have a pair of 3 or more jointed legs - from the Greek term arthron ( meaning joint) and podus (meaning foot) - they have an exoskeleton or hard outer body covering made up of chitin - the largest phylum in kingdom Animalia ARTHROPODS INVERTEBRATES 3. PHYLUM MOLLUSKA -they have soft body - from Latin term mollis, which means soft - most have protective shells as the outer covering MOLLUSKS INVERTEBRATES 4. PHYLUM ANNELIDA -characterized by ringlike body parts - they are worms with segmented body - they have a mouth at the front and anus at the tail end of their bodies - they have hearts and blood vessels that constitute a circulatory system ANNELIDS INVERTEBRATES 5. PHYLUM NEMATODA - roundworms are cylindrical worms with a finely tapered tail - the body is covered with a tough, non living skin that resist drying and crushing INVERTEBRATES 6. PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES - the simplest worm - some of them are free living while others are parasitic, living in the bodies of animals including humans FLATWORMS INVERTEBRATES 7. PHYLUM CNIDARIA - posses stinging structures called nematocysts in their tentacles - characterized by a hallow, tube like bodies, with a mouth at the end CNIDARIANS INVERTEBRATES 8. PHYLUM PORIFERA - pore-bearing organisms - they may live singly or in colonies - they eat by allowing water to flow through their bodies and trapping small organisms in the water using their specialized cells PORIFERANS