* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Things to Know while installing Linux OS
Linux adoption wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Object storage wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
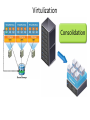
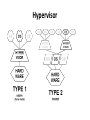
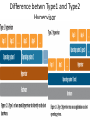
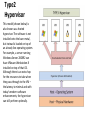
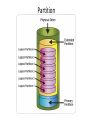
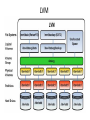
Things to Know while installing Linux OS Physical/Standalone • Physical server installation: 1. Automated installation: kickstart 2. Manual installation: vs Vitrulization Physical Server Physical Server Automated installation • Kickstart: Kickstart is the process to automatically perform unattended operating system installation and configuration. Manual installation 1. 2. access to hardware and install from dvd Out of band management tool: * ILO: hp's integrated lights out management tool * IDRAC: Dell's Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller * IMM: IBM management module * CIMC: Cisco Integrated Management Controller * ILOM: Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager for solaris * KVM-over-IP switch: Raritan Virtulization • Virtualization is the creation of a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, such as an operating system, a server, a storage device or network resources. • Virtual machines are nothing but software computer, which acts and performs like physical computers. Virtulization Virtulization To achieve virtulization we use a software called Hypervisor. • Hypervisor: A hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM) is a piece of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor is running one or more virtual machines is defined as a host machine. Each virtual machine is called a guest machine. • There are Two types of Hypervisor: *Type1 Hypervisor *Type2 Hypervisor Video Link` Definition Link Hypervisor Difference betwn Type1 and Type2 Hypervisor Type1 Hypervisor This type of hypervisor is deployed as a bare-metal installation. This means that the first thing to be installed on a server as the operating system will be the hypervisor. The benefit of this software is that the hypervisor will communicate directly with the underlying physical server hardware. Those resources are then paravirtualized and delivered to the running VMs. This is the preferred method for many production systems. Type1 Hypervisor • List of Type1 Hypervisors: *VMware vSphere / ESXi *Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V (or the free Hyper-V Server 2012) *Xen / Citrix XenServer *Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization (RHEV) * KVM Type2 Hypervisor This model (shown below) is also known as a hosted hypervisor. The software is not installed onto the bare-metal, but instead is loaded on top of an already live operating system. For example, a server running Windows Server 2008R2 can have VMware Workstation 8 installed on top of that OS. Although there is an extra hop for the resources to take when they pass through to the VM – the latency is minimal and with today’s modern software enhancements, the hypervisor can still perform optimally. Type2 Hypervisor • List of Type2 Hypervisor: • VMware Workstation, • VirtualBox, • VMware Fusion, • MED-V, • Windows Virtual PC, • Parallels, • MokaFive Installation in virtual machine • • • • Manual Clone Template Link for Video BootStages •BIOS •MBR •GRUB •KERNEL •INIT •RUNLEVEL Linux boot stages Link for boot stages boot stages • SAN : A Storage Area Network • Storage is an enterprise-level storage network of several (often, hundreds) of hard drives managed by an intelligent device. This allows for maximally efficient use of all available storage space, lowering total costs of ownership (TCO) and increasing return on investment (ROI). Most importantly, if a drive crashes, the your data is not lost!. Servers that host applications communicate with a SAN through fiber channel network equipment (iSCSI and F/C over IP are also supported), and the SAN determines where data is stored. If a hard drive fails for some reason, the other hard drives in the storage network essentially rebuild the data through a series of algorithms so no information is lost. DAS: Direct-attached storage is digital storage directly attached to the computer accessing it, as opposed to storage accessed over a computer network. Examples of DAS include hard drives, optical disc drives, and storage on external drives. Raid • RAID is an acronym for Redundant Array of Independent (or Inexpensive) Disks. In fact, RAID is the way of combining several independent and relatively small disks into a single storage of a large size. The disks included into the array are called array members. The disks can be combined into the array in different ways which are known as RAID levels. Each of RAID levels has its own characteristics of: • Fault-tolerance which is the ability to survive of one or several disk failures. • Performance which shows the change in the read and write speed of the entire array as compared to a single disk. • The capacity of the array which is determined by the amount of user data that can be written to the array. The array capacity depends on the RAID level and does not always match the sum of the sizes of the RAID member disks. To calculate the capacity of the particular RAID type and a set of the member disks you can use a free online RAID calculator. • http://mazzakolinux.com/raid-redundant-array-of-independent-disks/ RAID storage techniques • Striping - splitting the flow of data into blocks of a certain size (called "block size") then writing of these blocks across the RAID one by one. This way of data storage affects on the performance. • Mirroring is a storage technique in which the identical copies of data are stored on the RAID members simultaneously. This type of data placement affects the fault tolerance as well as the performance. • Parity is a storage technique which is utilized striping and checksum methods. In parity technique, a certain parity function is calculated for the data blocks. If a drive fails, the missing block are recalculated from the checksum, providing the RAID fault tolerance. Directory Vs Filesystem • Directory - a place where files and sub directories are stored • File System - is a directory which occupies separate space in the hard drive. In abstract sense, a filesystem is "something that has a capacity to hold files and directories". A filesystem might be contained in a disk partition (e.g. /dev/sda1), in a LVM logical volume (/dev/vg00/lvol1) or in a CDROM/DVD (/dev/scd0). Filesystem Type • • • • • • • • • Ext2 Ext3 ext4 Ntfs Fat32 xfs Linux File Systems: Ext2 vs Ext3 vs Ext4 Limitations of file system http://www.howtogeek.com/howto/33552/htg-explainswhich-linux-file-system-should-you-choose/ Disk Partition • An operating system like Windows / Linux can be installed on a single, unpartitioned hard disk. However, the ability to divide a hard disk into multiple partitions offers some important advantages. If you are running Linux on server consider following facts: • Ease of use - Make it easier to recover a corrupted file system or operating system installation. • Performance - Smaller file systems are more efficient. You can tune file system as per application such as log or cache files. Dedicated swap partition can also improve the performance (this may not be true with latest Linux kernel 2.6). • Security - Separation of the operating system files from user files may result into a better and secure system. Restrict the growth of certain file systems is possible using various techniques. • Backup and Recovery - Easier backup and recovery. • Stability and efficiency - You can increase disk space efficiency by formatting disk with various block sizes. It depends upon usage. For example, if the data is lots of small files, it is better to use small block size. • Testing - Boot multiple operating systems such as Linux, Windows and FreeBSD from a single hard disk. Partition types • Primary partitions is a partition that is needed to store and boot an operating system, In general, you would install the operating system in a primary partition. Maximum of four primary partition can exist. If we need more than four partition we can make Three primary partition and Make one Extended partition and many logical partition under Extended partition. Extended partition can be sub-divided into logical drives and is viewed as a container for logical drives, where data proper is located. An extended partition is not formatted. The extended partition is used only for creating a desired number of logical partitions. Logical partitions are the partitions that are created in the extended partition area. A logical partition is a way to extend the initial limitation of four partitions. An extended partition can contain up to 24 logical partitions. Partition Swap partition • Swap space in Linux is storage allocated from hard drive to act as • • if If virtual ram. Swap space in Linux is used when the amount of physical memory (RAM) is full. If the system needs more memory resources and the RAM is full, inactive pages in memory are moved to the swap space. While swap space can help machines with a small amount of RAM, it should not be considered a replacement for more RAM. Swap space is located on hard drives, which have a slower access time than physical memory. Swap space can be a dedicated swap partition (recommended), a swap file, or a combination of swap partitions and swap files. How to allocate swap: if n is amount of physical ram then, n <= 2 then swap = 2 x n for eg: if ram 2G then swap = 2x2=4G n > 2 then swap = 1 + n for eg: if ram 3G then swap = 1+3=4G LVM • In Linux, Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a device mapper target that provides logical volume management for the Linux kernel. Most modern Linux distributions are LVM-aware to the point of being able to have their root file systems on a logical volume. • Physical Volume • Volume Group • Logical Volume • In order to create a logical volume we need to follow a certain procedure. • Logical volume can only be created under Volume Group, and Volume group can only be created under Physical Volume. Physical volume can be created from partitions. • One partition equals to one physical volume. • Whole physical volume has to be give to one volume group • One volume group can be created from multiple physical volume • One volume group can contain multiple logical volume LVM LVM File sizes