* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faults brochure Een revised 9
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
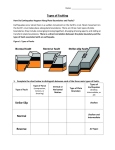
Faults Create a Brochure • You will use the information about faults to create a brochure that explains what a fault is and the types using examples. The brochure must contain pictures of each type of fault. It must be in color. Faults A fault is a large crack in the Earth's crust where one part of the crust has moved against another part. Title Definition Illustration Types of Stress: Types of Stress: Name three types Illustration of each Elastic Rebound Theory: Elastic Rebound Theory: Explain Parts of a Fault: Parts of a Fault: Labeled Drawing Inside Boundary Name of Stress Description ILLUSTRATION Boundary Name of Stress Description Boundary Name of Stress Description ILLUSTRATION Fault • A fault is a large crack in the Earth's crust where one part of the crust has moved against another part. This movement means that faults prove the Earth is an active place. They are signs of powerful forces deep underground. Types of Stress • Tensional – pulls rocks APART https://www.as.uky.edu/sit es/default/files/elearning/ module10swf.swf • Compressional – pushes rocks TOGETHER • Shearing – pulls rocks ALONG each other The Elastic Rebound Theory • Rocks will bend until they reach their Elastic Limit. • Then they will break (crack) – This forms a Fault Parts of a Fault Footwall Hanging Wall Normal Fault • form when the hanging wall drops down. The forces that create normal faults are pulling the sides apart, or extensional. Caused by Tensional Stress • Rocks/plates are pulled apart • Tension causes the hanging wall to fall down. • Divergent Boundary Normal Fault Normal Fault Normal Fault Reverse Fault • Form when the hanging wall moves up. The forces creating reverse faults are compressional, pushing the sides together. Caused by Compressional Stress • • • • Rocks/plates are pushed together. Causes the Hanging wall to move up. Earthquakes!!!! Convergent Boundary Reverse Fault Reverse Fault Strike-Slip Fault • have walls that move sideways, not up or down. That is, the slip occurs along the strike, not up or down the dip. • Strike-slip faults are either right-lateral or left-lateral. That means someone standing near the fault the far side move to the right or to the left, respectively. The one in the picture is left-lateral. Caused by Shearing Stress • • • • Rock/plates are sliding in opposite directions. Movement is only horizontal. EARTHQUAKES!!! Transform Boundary Strike Slip Fault Strike – Slip Fault