* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review of Basic Algebra Skills
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Polynomial greatest common divisor wikipedia , lookup
Polynomial ring wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Eisenstein's criterion wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
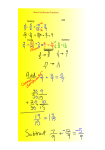
REVIEW OF BASIC ALGEBRA SKILLS Math 3 What do you need? • Adding and Subtracting Polynomials • Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Dividing Fractions • Solving Equations of Different Forms • Identifying Graphs • Domain and Range Basic Vocabulary Coefficient: A number used to multiple a variable. Constant: A fixed value. Variable: A symbol for a number we don’t know yet. Operator: A symbol that shows an operation (add, subtract, etc.) Basic Vocabulary Expression: Numbers, symbols, and operators grouped together that show the value of something. Equation: An equation says that two things are equivalent. Term: In algebra, a term is either a single number or variable, or numbers and variables multiplied together • Terms are separated by addition and subtraction signs Adding and Subtracting Polynomials A polynomial is an expression that has more than one term. When adding or subtracting polynomials, it is important to identify the “like terms”. Like terms are terms whose variables and their attached exponents are the same. When adding or subtracting polynomials, identify which terms are similar and add them together (keeping the signs). ***Be careful when dealing with minus! Adding and Subtracting Polynomials (2x2 + 6y + 3xy) - (3x2 - 5xy - x) + (6xy + 5) Take a minute and simplify the above Operations on Fractions Adding and Subtracting Do the fractions have the same denominator? If yes, add or subtract the numerators. If no, is one denominator a multiple of the other? -If yes, multiply the numerator and the denominator by the same number so that the denominators are the same. -If no, multiply the numerator and denominator of each fraction by the denominator of the other fraction. Multiplying Write the prime factorization of the numerators and denominators of each fraction. Cross out pairs of common prime factors that are diagonal from each other. Multiply straight across. Dividing Keep-Change-Flip, and then follow same procedures from “Multiplying” Solving Equations A solution is a value we can put in place of a variable which makes the equation true. When solving for a missing variable you need to utilize the “inverse operations”. An inverse operation reverses the effect of another operator. • Addition and Subtraction • Multiplication and Division • Square and Square Root • Cube and Cube Root • Sine and Arcsine Solving Equations Order of Operations Methodology Methodology Distribute Combine like terms Move variable to one side Undo addition/subtraction Undo multiplication/division Solve equations examples 2𝑥 + 1 = −17 7 𝑥 − 1 = 21 5𝑥 + 2 = 2𝑥 + 17 5 𝑥 − 4 = 3𝑥 + 2 𝑥+1 =7 3 3(𝑥 − 1) =6 5 Domain and Range The domain of a function is the set of all x-values that are included in the function’s parameters. The range of a function is the set of all y-values that are included in the function’s parameters. Domain and Range Some questions will ask you to look at a graph and tell the domain and range. While others will require that you read the equation and discover these parameters. Domain and Range from the Graph Domain and Range from the Function Set Notation vs. Interval Notation “All numbers greater than 0” Interval Notation Set Notation • Uses brackets and/or parentheses • Set notation uses curly brackets • • The first space tells us what variable we are talking about Tells us the upper and lower bounds that are used in the domain/range • Utilizes “unions” to talk about multiple intervals that are true for the function • Parentheses imply the number is NOT being used, while brackets imply the number IS being used. • If you wish to say that there is no limit to the domain or range, you can use positive and negative infinity. • • The line means “such that” The last space tells us the restriction on the variable. Domain and Range Examples By the Graph By the Function 3 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 Tip: What do you know about division?