* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY
History of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Clinical decision support system wikipedia , lookup
Collaborative information seeking wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Time series wikipedia , lookup
Knowledge representation and reasoning wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
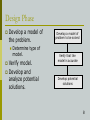
Using Information Systems for Decision Making (Week 13, Thursday 4/5/2007) BUS3500 - Abdou Illia, Spring 2007 1 LEARNING GOALS Explain the decision-making process. Describe decision support systems. Explain how Group Decision Support Systems work. Describe executive information systems. Describe Expert Systems and Knowledge Work systems. 2 Recall from previous classes Types of Information Systems: Top Management Office Office workers workers - Transaction Processing Systems Office Automation Systems Knowledge Work Systems Management Information Systems Decision Support Systems Executive Information Systems Middle Management Office workers Knowledge workers Office workers Questions Lower Management Operational workers Q: What kind of IS are designed to provide help for decision makers? Q: What criteria we should look at to distinguish between (1) IS for decision making and (2) other IS? 3 Systems for Decision Making Task structure Degree of level repetitiveness Unstructured Type of Information System used EIS, KWS Non-repetitive DSS Semi-structured TPS Structured Repetitive 4 Systems for Decision Making Decision support systems (DSS) are one tool A computer-based system that supports and improves human decision making Helps middle managers analyze complex problems Group decision support systems (GDSS) Executive information system (EIS) Tool for supporting team decision making Computer-based system that supports the decisionmaking processes of senior managers Knowledge Work Systems (KWS) Computer-based system that supports the decisionmaking processes of Knowledge workers 5 The Decision-Making Process Simon’s model of the decision-making process Intelligence Design Choice 6 Intelligence Phase Scan the environment for a problem. Determine if decisionmaker can solve the problem. Within their scope of influence? Fully define the problem by gathering more information about the problem. Data source Scan Environment for problem to be solved or decision to be made Problem ? No MIS END Yes Problem within scope of influence? No END Yes Gather more information about the problem Internal & External data 7 Design Phase Develop a model of the problem. Determine type of model. Verify model. Develop and analyze potential solutions. Develop a model of problem to be solved Verify that the model is accurate Develop potential solutions 8 Choice Phase Select the solution to implement. More detailed analysis of selected solutions might be needed. Verify initial conditions. Analyze proposed solution against real-world constraints. 9 Decision Support Systems Designed to help individual managers make decisions Major components Data management subsystem Model management subsystem Internal and external data sources Typically mathematical in nature User Interface Model Management - Sensitivity Analysis -> What-if Analysis -> Goal-seeking Analysis User interface How the people interact with the DSS Data visualization is the key Text Graphs Charts Data Management - Transactional Data Data warehouse Business partners data Economic data 10 Modeling Tools and Techniques Simulation is used to examine proposed solutions and their impact Sensitivity analysis Determine how changes in one part of the model influence other parts of the model What-if analysis Manipulate variables to see what would happen in given scenarios Goal-seeking analysis Work backward from desired outcome 11to Determine monthly payment given various interest Works backward from a given monthly payment rates. determine various loans that would give that payment. Groups Decision Support Systems Designed to support groups make decisions with the help of a Group Facilitator GDSS Tools: Brainstorming tools: Allow users enter ideas simultaneously & anonymously Commenter tools: Allow users to anonymously comment on others’ ideas Categorizing tools: Groups ideas into categories Idea-ranking tools: Ranks ideas. Identify the best ones. Electronic-voting tools: Allow users to vote for their favorite ideas. Front Screen GDSS tools 12 Executive Information Systems Computer-based tool that specifically helps top-level management make strategic decisions Processes both internal and external data Presents data in summary form Drill-down is a key feature – gives the manager the ability to see more details when needed 13 14 KWS: Expert Systems Artificial Intelligence systems that codify human expertise in a computer system Main goal is to transfer knowledge from one person to another Wide range of subject areas Medical diagnosis Computer purchasing Knowledge engineer elicits the expertise from the expert and encodes it in the expert system 15 Expert Systems Components Knowledge base: database of the expertise, often in IF THEN rules. Inference engine: derives recommendations from knowledge base and problem-specific data User interface: controls the dialog between the user and the system Explanation system: Explain the how and why of recommendations User Domain Expert Expertise Knowledge Engineer Encoded expertise Knowledge base Example of rules User Interface Inference Engine Explanation System System Engineer IF family is albatross AND color is white THEN bird is laysan albatross. IF family is albatross AND color is dark THEN bird is black footed albatross 16 Other KWS Neural networks – use software to simulate the neural working of the human brain Intelligent agents (bots) – autonomously handle tasks for humans and act on user’s behalf Genetic algorithms – Computer instructions that create a population of thousands on potential solutions and evolves the population toward better solutions Fuzzy logic – a way to get computers to come closer to the ability to see fine distinctions, not just ones and zeros 17 Summary Questions Malaga Notes 1) What are the steps of a decision making process according to the Simon’s model? Explain each step. 6-9 2) (a) What are the major components in a DSS? (b) What is the function of each? 10 3) (a) What is the difference between a DSS and a GDSS? What is a Group facilitator? What are the main tools used in a GDSS to help users reach a decision? 4) What is an EIS? What is the difference between a DSS and an EIS? 5) What is an Expert System? What are the main components of an Expert system? What is a knowledge engineer? 10,12 14 16 18