* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Garden Botany ()
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
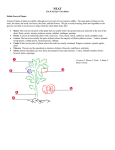
Garden Botany Definitions • Botany is the science or study of plants • Horticulture is the science and art of cultivating flowers, fruits, vegetables, grass, and ornamental plants in an orchard, garden, nursery or greenhouse. • From the Latin: Hortus (garden) and cultus (tilling) Classifying Plants • Classification by: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Use Temperate Requirement Ecological Adaptation Taxonomy Stem and leaf structure Life Cycle Classification by Use • EDIBLE – Fruits • Tree fruits • Small fruits – Vegetable • Warm season • Cool season – Herbs • Culinary • Medicinal – Nuts • ORNAMENTAL/LANDSCAPE – Woody Plants • Trees • Shrubs • Vines and ground covers – Herbaceous Plants • Flowers • Vines and ground covers – Grass Classification by Temperate Requirement • • • • • Tropical plants vs. Temperate-zone plants Warm vs. Cool season plants Tender vs. Hardy plants Long day vs. Short day plants Cold hardiness zone plants Classification by Ecological Adaptation • • • • • • Alpine Prairie Ponderosa pine forest Pinyon/Juniper forest Riparian Xeric (dry) Classification by Taxonomy • Plant Kingdom divided into two groups: – Non-vascular plants – Vascular plants • Nearly all plants in the garden are vascular Classification by Taxonomy • Gymnosperms – Do not have true flowers – Seeds are enclosed in fruits – Most seeds are produced in cones Classification by Taxonomy • Angiosperms – Produce flowers – Develop fruits that contain seeds – Can be divided into monocots and dicots Classification by Taxonomy Plant Evolution Classification by Stem and Leaf Texture • • • • • • • Herbaceous plants Woody plants Deciduous plants Evergreen plants Broadleaf Narrowleaf Grass-like Butterfly Bush, Woody stems Bee Balm, Herbaceous/non-woody stems Evergreen plants hold their leaves year-round Corn is a good example of broadleaf Deciduous plants shed their leaves every year Narrow leaf lavendar Classification by Life Cycle • Annuals • Biennials • Perennials PLANT PARTS • Roots • Stems • Leaves • Fruits • Flowers • Seeds Roots • Absorb water and nutrients from soil • Anchor the plant • Provide support for stem • Store sugars and starches (needed for photosynthesis) • Source of winter survival for perennials • Fibrous roots vs. Tap roots Stems • Connects roots to leaves • Supports buds and leaves • Phloem and xylem serve as channels in the stem for carrying water, minerals, and sugars to other plant parts. Xylem brings water up the stem, and Phloem sends water down. • Stems grow above or below the ground. Leaves • Absorb sunlight energy to make food through the process of photosynthesis • Take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen • Store energy • Control water through transpiration • Simple or compound Photosynthesis water + CO sugar + O 2 2 Flowers • Showiest part of plants; fragrant and/or colorful to attract pollinators • Important for sexual reproduction • Self pollinating or cross pollinating Fruit • Part of the plant that surrounds one or more seeds • Spread seeds • Attracts animals to help spread seeds Seeds • Contain the information needed for a new plant to grow • Embryo • Endosperm • Seed coat