* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar: Conjunctions
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Classical compound wikipedia , lookup
Lojban grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Contraction (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
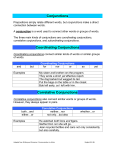
Grammar: Conjunctions & Interjections What do they do? Conjunctions join words or groups of words. There are several types of conjunctions: Coordinating conjunctions Correlative conjunctions Subordinating conjunctions Coordinating Conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions join words or groups of words that are equal in importance. Example: Thunder, lightening, and hail hit the area. The thunder and lightning finally stopped, but the hail kept falling. Remember FANBOYS: F: For A: And N: Nor B: But O: Or Y: Yet S: So Correlative Conjunctions Correlative Conjunctions are always used in pairs (they correlate). The words or phrases joined by a correlative conjunction should play the same role in the sentence. For example, the conjunction might join two subjects or two clauses. Example: Either its raining or snowing. Both you and I are going dancing. Examples: Both…and Either…or Neither… nor Not only…but also Whether…or Just as…so (too) Subordinating Conjunctions Subordinating conjunctions connect adverb clauses to main clauses Adverb Clause: a subordinate clause that functions as an adverb. It modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. Example: The rain fell sooner than we had expected. (modifies the adverb sooner) The animals seemed nervous whenever rolling thunder began. (modifies the adjective nervous) Example: (after, although, as far as, as long as, when, where, whereas, while, if, etc.) The author smiled because a reader asked for her autograph. We studied together so that we could all pass the test. Interjections Interjections express mild or strong emotion. No grammatical connection to the rest of the sentence. They are set off by a comma or an exclamation point. Examples: aha, ouch, cool, hey, hooray, oh, ouch, ugh, well, wow, yo, etc. Example: Darn! I forgot my book again. No Way! I certainly will not do that. She explaimed, “Wow! What a parade!”