* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
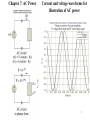
Download Figure 7.1, 7.2
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Captain Power and the Soldiers of the Future wikipedia , lookup
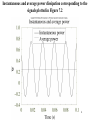
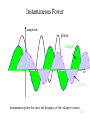
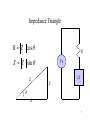
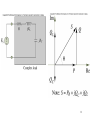
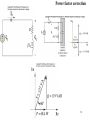
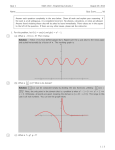
Chapter 7: AC Power Current and voltage waveforms for illustration of AC power Figure 7.1, 7.2 1 Instantaneous and Average Power p(t ) v(t )i (t ) VI cos(t ) cos(t ) VI VI P(t ) cos( ) cos(2t ) 2 2 1T 1 T VI 1 T VI Pav p(t )dt cos( )dt cos(2t )dt T0 T0 2 T0 2 VI 1 V2 cos( ) cos (Average Power) 2 2 Z 2 Instantaneous Power Calculations p vi in watts vt Vm cos(t v ) p it I m cos(t i ) Vm I m V I V I cos( v i ) m m cos( v i ) cos 2t m m sin( v i ) sin 2t 2 2 2 v is the voltage phase angle i is the curent phase angle 3 Instantaneous and average power dissipation corresponding to the signals plotted in Figure 7.2 Figure 7.3 4 Instantaneous Power magnitude power voltage wt current Instantaneous power has twice the frequency of the voltage or current 5 RMS Value • It is customary in AC power analysis to employ the RMS value of the AC voltage and currents in the circuit (Read Section 4.2). Vrms V 2 I I rms Pav ~ V ~ I 2 ~ 2 V Z ~ ~ cos V I cos 6 Impedance Triangle R Z cos R X Z sin Z Vs jX X R 7 Power Factor • The phase angle of the load impedance plays a very important role in the absorption of power by a load impedance. • The average power dissipated by an AC load is dependent on the cosine of the angle of the impedance. • The term cos () is referred as the power factor (pf). • The power factor is equal to 0 for purely inductive or capacitive load. • The power factor is equal to 1 for a purely resistive load. 8 Complex Power Apparent Power S Q Reactive Power Pav Real Power ~ ~ S Pav2 Q 2 V I ~ ~ Pav V I cos ~ ~ Q V I sin 9 Table 7.2 10 Figure 7.16, 7.17 11 Power factor correction Figure 7.18, 7.19, 7.20 12