* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Serious skin infections
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
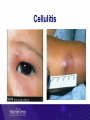
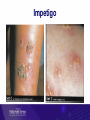
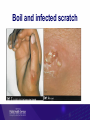
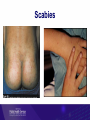
Healthy skin and Skin infections Objectives Introduction and background Toi Te Ora goals and analysis Serious skin infections Key prevention messages and resources Functions of skin Skin is an amazing organ: Covers and protects Helps to maintain correct temperature Sense of touch Skin also protects against infections However, the skin may become infected leading to serious health problems Serious skin infections Serious skin infections (SSI) are a significant cause of avoidable hospitalisations in NZ SSI includes cellulitis, impetigo and abscesses Can affect the blood, kidneys, bones, joints, lymph nodes and brain Toi Te Ora – Public Health Service Goals Reducing skin infections 3 key strategies: 1. Increasing community awareness 2. Increasing skills, capacity and responsiveness of health professionals 3. Improving responsiveness and effectiveness of primary and community health services Area served by Toi Te Ora Defining Serious Skin Infection “A child aged 0-14 years, admitted to hospital with a principal or additional diagnosis of serious skin infection, with a diagnosis code either within the ICD skin infection sub-chapter, or within the categories of skin infection of an atypical site or skin infection following primary skin disease or external trauma.” (O’Sullivan & Baker, 2010, p181) Category A – Skin infections of typical sites L01.0, L01.1 L02.0 to L02.9 inclusive L03.01 to L03.9 inclusive L04.0 to L04.9 inclusive L05.0 L08.0 L08.1, L08.8, L08.9 Impetigo Cutaneous abscess, furuncle and carbuncle Cellulitis Acute lymphadenitis Pilonidal cyst with abscess Pyoderma Other infections of skin and subcutaneous tissue Category B – Skin infections of atypical sites A46 H00.0 H60.0 to H60.3 inclusive, H62.0, H62.4 Erysipelas Hordeolum/cellulitis/abscess eyelid Abscess/cellulitis external ear and infective otitis externa J34.0 K61.0 Abscess/cellulitis nose Anal abscess/cellulitis (excludes rectal, ischiorectal or intersphincteric regions) Acute inflammation/cellulitis/abscess of orbit Other inflammatory disorders of penis, scrotum and unspecified male genital organ(excludes deeper tissues) Abscess/cellulitis of vulva H05.0 N48.2, N49.2, N49.9 N76.4 Category C – Skin infections secondary to primary disease of the skin B01.8 B86 L30.8,L30.9,L30.30 Varicella with other complications Scabies Dermatitis unspecified and other specified (eczema) and infective eczema Category D – Skin infections secondary to trauma S10.13, S10.83, S10.93, S20.13, S20.33, S20.43, S20.83, S30.83, S30.93, S40.83, S50.83, S60.83, S70.83, S80.83, S90.83, T00.9, T09.03, T11.08, T13.03, T14.03, T63.3, T63.4 Insect/spider bites T79.3 Post-traumatic wound infection not elsewhere classified T89.01,T89.02 Open wound infection with foreign body (+ infection) and open wound with infection Data Analysis Hospital discharge data were obtained from the Ministry of Health The data included all children in New Zealand aged 0-14 The same filters that O’Sullivan and Baker (2011) used were applied to the data: Day cases were removed – (discharge that had a length of stay of less than 1 day) Transfers – any discharge data that was classified as a transfer was removed Readmissions – discharges within 30 days of previous discharge with the same principle diagnosis were removed Overseas visitors – Data for non-residents were removed from the dataset Incidence of Serious Skin Infection Incidence by Age Incidence by Ethnicity Incidence by Category Incident Cases by CAU Census Area Unit Kawerau District Kawerau Te Puke Community East Whakatane North Opotiki Yatton Park Whakatane West Hairini Gate Pa Trident Tauranga Central Murupara Greerton Western BOP Whakatane Opotiki Tauranga Whakatane Tauranga Tauranga Whakatane Tauranga Whakatane Tauranga Percentage 6.6 5.1 4.5 4.3 3.8 3.3 3.0 2.8 2.8 2.7 2.3 2.1 Tip of the Iceberg In Tairawhiti DHB it is estimated that for each incident case of serious skin there are a further 14 cases of skin infection seen in primary care (O’Sullivan, 2011) It is likely to be a similar situation in Bay of Plenty DHB Summary Incidence of serious skin infection in Bay of Plenty DHB is higher than the incidence of New Zealand Younger children are more likely to have a serious skin infection There is a large inequality between Maori and Non-Maori We can identify the census area units where a disproportionate number of the cases come from Serious skin infection represents the tip of the iceberg Common SSIs Cellulitis Cellulitis is an acute bacterial infection of the soft tissues of the skin. The infection spreads causing the skin and layers underneath to become red, swollen and tender Cellulitis Causes Any area of skin can become infected if skin is broken, e.g. from a sore, insect bite, boil, rash, cut, burn or graze Most common pathogens Staph.aureus, Strep.pyogenes, Group C and G strep Management Cellulitis is a serious infection that needs to be treated with antibiotics Keep area elevated Periorbital / severe cellulitis refer to hospital Consider swab of moist lesion if high risk of recurrence or MRSA Impetigo Impetigo (or school sores) is characterised by small infectious blisters, which later develop a honey coloured scab like crust Impetigo Causes May be caught from other person with impetigo or boils or may ‘appear out of the blue’ Often starts at sight of minor injury Most common pathogens Strep.pyogenes, Staph.aureus Management Consider swab of moist lesion if risk of recurrence or complicated factors Localised staph infections may be managed using wound care and antiseptics for local application Routine use of topical antibiotics e.g. fucidic acid or mupirocin is not advised due to increasingly resistant forms of staph Boils / abscess Boils are a deep infection of the hair follicles and present as one or more tender red spots, lumps or pustules An abscess is a cavity containing pus which may also have surrounding cellulitis of the skin and tissue Staph aureus is common pathogen Boil and infected scratch Management Swab at least one moist lesion Localised infections can be managed with wound care (including I&D of large boils & abscesses) Routine use of topical antibiotics e.g. fucidic acid or mupirocin is not advised due to increasingly resistant forms of staph Use a/bs if fever, cellulitis or co-morbidity e.g. eczema Scabies Scabies is a skin infestation that can be passed easily between people Caused by tiny mites The mites burrow into the upper layers of the skin and lay eggs along the way Small blisters, red spots and itchy red patches form on the skin above the burrows Causes Almost always acquired by skin to skin contact Occasionally acquired by bedding or furnishing – as mite can survive few days off human host Symptoms Rash small areas of red, itchy bumps and blisters most often noticed: Between the fingers On the wrist On the elbow Around the waist On the bottom and private parts Can lead to secondary infection Scabies Treatment Scabicides – chemical insecticides used to treat scabies In NZ most common are: 5% Permethrin cream 0.5% Aqueous malathion lotion, left for 24 hours See scabies fact sheet Treatment and prevention All people living in the household, and other close contacts, should be treated at the same time whether or not they have symptoms of scabies On the same day as applying the treatment, all clothes worn against the skin in the last 3 days must be washed in hot water and dried Bedding and towels Sheets, pillowcases, towels and face-cloths should also be washed in hot water It is not necessary to wash blankets, duvets or quilts, you can just hang them out in the sun for a day Key prevention messages Skin infections are preventable If left untreated skin infections can lead to serious health problems Serious skin infections are a major cause of avoidable hospitalisations in New Zealand Healthy skin messages Wash and dry hands with soap and water often Keep skin clean with regular showers Clean wounds and hands, Cut fingernails and Cover injuries Healthy skin messages Healthy food and adequate sleep is important for healthy skin Skin infections often start with an insect bite – treat animals for fleas regularly Wear clean clothes Keep house clean inside and out Wash sheets and towels regularly Action messages Families / whanau / individuals should be advised to seek medical attention if a sore or area of redness has any of the following features…. Action messages Is greater than the size of a ten cent coin (approximately 1.5cm) Increasing size Has pus Has red streaks coming from it Is not getting better within two days Is located close to the eye www.healthshare.health.nz/public/skin-conditionsresources Further information… Healthy skin resources are available to download from : http://www.ttophs.govt.nz/healthyskin_resourc es http://www.healthliteracy.org.nz/researchand-projects/ www.healthshare.health.nz/public/skinconditions-resources