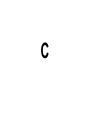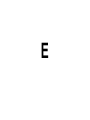* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard 19
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Pearl Harbor (film) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Standard 19 The student will identify the origins, major developments, and the domestic impact of World War II, especially the growth of the federal government. A A. Philip Randolph • He fought for civil rights during the 1930’s and 1940’s. • He proposed a march on Washington D.C. to protest the discrimination that was occurring in the US. • FDR issued Executive Order 8802 to prevent the march and help African Americans. – The order assured fair hiring practices for any job that was funded with government money. – It also created the Fair Employment Practices Committee to enforce the order. • An African American who benefited from the Fair Employment Act would be most thankful for the efforts of A. B. C. D. Winston Churchill Dwight Eisenhower A. Philip Randolph Douglas MacArthur • Although his proposed march on Washington did not happen, his boldness still inspired President Roosevelt to back legislation prohibiting discrimination in the national defense industry. Who was he? A. B. C. D. Martin Luther King, Jr. Robert Kennedy A. Philip Randolph Jackie Robinson B Japan Attacks Pearl Harbor • December 7, 1941 Japanese planes bombed and strafed the fleet and airfields nearby. • In less than 2 hours, 2,400 Americans had been killed and nearly 1200 wounded. • Nearly 300 warplanes were damaged or destroyed and 18 warships had been sunk or heavily damaged. • Pearl Harbor is the reason the US enters World War II. Internment Camps • These were created to imprison JapaneseAmericans during the war. – The Japanese-Americans were held in the camps for the entirety of the war. – Racism was the main reason for their continued imprisonment. • German-Americans and Italian-Americans were held in camps at the beginning of the war. – They were released later during the war and these two groups were no longer imprisoned. • President Roosevelt referred to December 7, 1941 as, “… a day that will live in infamy…” because it was A. B. C. D. The day Allied troops invaded France. The day marking the fall of France. The day Berlin fell to the Soviets. The day the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor. • What was the result of the attack on Pearl Harbor? A. An American declaration of war on Japan B. The complete destruction of the US Navy C. Renewed efforts in Europe to rid the region of Hitler’s dominance D. Continued isolationism and a belief that American soldiers should stay state-side • What was the purpose of US internment camps? A. To protect Japanese, German, and Italian American citizens from racists who might harm them B. To provide a place to train soldiers to fight in WWII C. To allow a secluded place for scientists to work on the atomic bomb D. To keep a close eye on citizens who might be a threat to the US war effort • The US entered the fighting in World War II specifically because of what event? A. Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor B. Germany’s invasion of Poland C. Germany and the USSR’s non-aggression pact D. The fall of France • In order to achieve their goal of annexing territories rich in raw materials and natural resources, the Japanese had to first eliminate the threat of the US Pacific Fleet. This reality led to A. B. C. D. An invasion of the Philippines. The use of kamikaze pilots. The decision to bomb Pearl Harbor. Japan’s decision to use the atomic bomb. C American Involvement Grows • Congress passed the Lend-Lease Act in March 1941. • It allowed the President to give aid to any country that we felt was vital to the security of America. – Those countries are Great Britain, France, and Russia. The Two Sides • The Axis Powers – Germany – Japan – Italy • The Allies – – – – Great Britain France Russia USA Battle of Midway • This was the turning point of the war in the Pacific. • The US had decoded the Japanese plans and was ready for the attack. • The US effectively destroyed Japan’s power and ability to further threaten the Pacific. – Japan was forced to go on the defensive. Preparation for the D-Day Invasion • The allies began to build up troops in southern England. • In response, the Germans built up their defenses along the French coastline. • The Germans added machine-gun bunkers, barbed wire fences, land and water mines, and underwater obstructions. Operation Overlord (D-Day) • June 6, 1944 • 1st – American and British paratroopers were dropped behind enemy lines at night. • 2nd – Allied warships and planes shelled the coast. • 3rd – 150,000 Allied troops came a shore along 60 miles of Normandy coast. The Fall of Berlin • The Soviet Union approached the German capital from the East as the Allies came from the West • The fall of Berlin was a significant symbol for the end of the war and victory over the Nazis • The city was controlled by all four major allies, and eventually was divided into zones of control that became East and West Berlin • In 1944, journalist Ernie Pyle wrote, “It seems to me a miracle that we ever took the beach at all.” What can you infer about D-Day from this statement? A. There were not enough soldiers and machines to go to war. B. It was a long, bloody, and very difficult battle. C. The US was unprepared. D. The beach terrain was difficult. • What three nations were part of the Axis Powers? A. B. C. D. Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union Japan, China, and the Philippines The US, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union Germany, Italy, and Japan • What effect did the Battle of Midway have? A. It prompted Hitler to commit suicide. B. It enabled the Allies to finally open a second front in Western Europe. C. It turned the tide of the war in the Pacific in the US’ favor. D. It gave Japan the upper hand, but only briefly. • Who would have been most excited about the US’ Lend-Lease Act? A. B. C. D. Germany Japan Great Britain Italy D Rationing and Conservation • During World War II, all Americans were asked to reduce the amount of food, fuel, metal, and rubber that they used. – Rationing meant that you were only given a set amount of a particular item. – Conservation called for people to reduce their consumption on their own. Women in the Armed Forces • 275,000 women volunteered for military service. • Women were used in all areas except combat. • Women began to develop a want to work outside the household and led to many women joining the workforce after the war • Which word describes the homefront during World War II? A. B. C. D. Easy Selfish Sacrifice Uncooperative E Los Alamos • The Manhattan Project was created to invent the first atomic bomb. • Enrico Fermi and Albert Einstein worked together on the project. • On July 16, 1945, the first atomic bomb was detonated. • It created a huge crater and shattered windows 125 miles away. Japan Surrenders • The US dropped an atomic bomb on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945. • The 2nd was dropped on Nagasaki three days later. • August 14, 1945, Japan surrenders. • A scientist assigned to a project in Los Alamos, New Mexico in 1945 was most likely busy working on A. B. C. D. The War Production Board. The Manhattan Project. The V-E Project. Operation Overlord. • What event was a direct result of the Manhattan Project? A. D-Day B. Stalin’s decision to try and force western nations out of Berlin. C. Hitler’s decision to persecute the Jewish people. D. Dropping of the atomic bomb. Unit 4 Book Questions • • • • • • • • Pg. 654: 1-9 Pg. 698: 1-10 Pg. 728: 1-8 Pg. 766: 1-9 Pg. 798: 1-8 Pg. 842: 2-4, 8, 9, and 11 Pg. 878: 1-9 Pg. 1014: 1-9