* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alternating Current - School
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Fuse (electrical) wikipedia , lookup
Overhead line wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
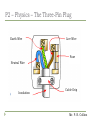
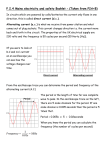
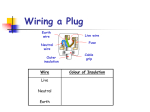
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MrNdMoiMh-Q P2 - Physics Mains Electricity P2 – Physics - Aims to recognise errors in the wiring of a three-pin plug to recognise dangerous practice in the use of mains electricity to compare potential differences of d.c. supplies and the peak potential difference of a.c. supplies from diagrams of oscilloscope traces (HIGHER ONLY) to determine the period and hence the frequency of a supply from diagrams of oscilloscope traces Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics – Mains Electricity Mains electricity is useful but can be very dangerous. It is important to know how to use it safely Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics – Currents Cells and batteries supply current which always passes in the same direction. This is called direct current (d.c.) An alternating current (a.c.) is one which is constantly changing direction. Mains electricity is an a.c. supply. In the UK it has a frequency of 50 cycles per second (50 hertz) UK mains supply is about 230 volts Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains using cable and a three-pin plug Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics - Currents Voltage Direct Current – flows in one direction only Time 1/50th second 230V Time Alternating Current – changes direction 50 times every second (frequency = 50 hertz) Voltage Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics – The Three-Pin Plug Earth Wire Live Wire Fuse Neutral Wire Insulation Cable Grip Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics – The Three-Pin Plug The neutral wire of a plug stays at a potential close to zero with respect to the earth The live wire of a plug alternates between positive and negative potential with respect to the neutral wire Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics - Safety If an electrical fault causes too great a current the circuit should be switched off by a fuse or a circuit breaker When the current in a fuse wire exceeds the rating of the fuse it will melt, breaking the circuit Appliances with metal cases are usually earthed The earth wire and fuse together protect the appliance and the user Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics - Earth wires Earth wires are always used if an appliance has a _____ case. If there is a _____ in the appliance, causing the live wire to ______ the case, the current “_______” down the earth wire and the ______ blows. Words – fuse, fault, metal, surges, touch Mr. P. R. Collins P2 – Physics - Fuses Fuses are _______ devices. If there is a fault in an appliance which causes the ____ and neutral (or earth) wire to cross then a ______ current will flow through the _____ and cause it to _____. This will break the _______ and protect the appliance and user from further _____. Words – large, harm, safety, melt, live, circuit, fuse Mr. P. R. Collins