* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sunspots
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Energetic neutral atom wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Solar phenomena wikipedia , lookup
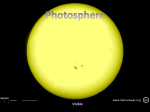
Sun phenomena sunspots • By tracking them, we realized the sun rotates • Click here Sunspot up close What causes sunspots? • The magnetic field gets twisted inside the sun • Click here Sunspots are ticking time bombs that lead to explosions on the sun’s surface • Coronal loops / coronal arches • Solar flares • Solar prominences AKA Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) Coronal loops- gases held up in a magnetic loop—reach from sunspot to sunspot Solar Flare- a magnetic storm that explodes huge amounts of particles and gases STRAIGHT OUT from the surface of the Sun. Solar prominence—a MASSIVE arc of gas & particles that erupt from the surface of the Sun Solar prominence – AKA coronal mass ejection (CME) Coronal mass ejection CME • balloon shaped plasma burst • An ejection from August 2012: • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GrnGiq6iWc&feature=player_embedded#! Prominence/CME--Look at the size of Earth! Solar wind • streaming electrically charged atomic particles that constantly escape from the Sun through coronal holes, which are weak spots in the Sun’s magnetic field. • It is faster and much hotter than Earth’s wind. • Solar wind is traveling at about 1 million miles an hour by the time it gets close to Earth. • If it blew on the Earth’s surface, it would obliterate all life, but Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere protect the planet. • Click here NOTES Sun- average age and average temperature star that is a bit on the small side • Cycle of solar activity- 11 year cycle of sunspots -Sunspot- cool, dark area on the sun [like a ticking time bomb that will explode some day] created by twisted magnetic fields -showed us the sun rotates Where is sunspot maximum & minimum? • Solar flare- explodes from sunspot and goes into space (several per day to 1 per 2 weeks) –Messes up tv, radio, cell phones, aviation and space communications –Flares interact with earth’s ionosphere making auroras »Aurora borealis- northern lights »Aurora australis- southern lights • [HOW? nutrinos from solar flares follow magnetic field then charged particles collide with particles in ionosphere creating light. Sound is claimed by some as well] click here and here • Coronal loop- arching column of gas that follows magnetic lines (doesn’t leave Sun) • Prominence/Coronal Mass Ejection – CME Massive explosion from the sun that ejects ten billion tons of mass (protons) and energy into space Sun’s layers • Core- fusion occurs here • Radiative zone- electromagnetic waves (energy) bounce around like a pinball, taking a million years to escape • Convection zone- heat rises and cold sinks • Photosphere- visible surface of the sun • Chromosphere- the bottom of the sun’s atmosphere (see through) • Corona (crown)- the top of the sun’s atmosphere (see through) Great website • http://ircamera.as.arizona.edu/NatSci102/Nat Sci102/lectures/sun.htm