* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hypothyroid - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
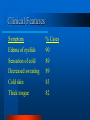
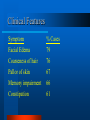
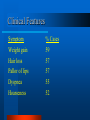
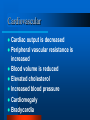
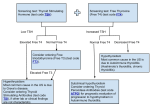
Clinical Application Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism Gail Nunlee-Bland, M.D. Hypothyroidism Clinical condition associated with decreased function of the thyroid gland and a decrease in the circulating level of thyroid hormones Hypothyroidism Causes Three categories – permanent loss or atrophy of thyroid tissue (primary hypothyroidism) – compensatory thyroid enlargement due to transient or progressive impairment of hormone biosynthesis (goitrous hypothyroidism) – insufficient stimulation of a normal gland as a result of hypothalamic or pituitary disease (secondary hypothyroidism) Primary Atrophic Hypothyroidism Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s disease) Postablative I 131 or surgery Athyreotic due to ageneisis or dysplasia Unresponsivenes to TSH Goitrous Hypothryoidism Hashimoto’s thyroiditis Endemic iodine deficiency Iodine-induced Antithyroid agents Central Hypothyroidism Secondary (pituitary) hypothyroidism Panhypopituitarism Isolated TSH deficiency Abnormal TSH synthesis or receptor defect Hypothalamic hypothyroidism Autoimmune Thyroiditis More common in women Thyroid autoantibodies present – autoantibodies to thyroid peroxidase (TPOAB) – autoantibodies to thyroglobulin (TgAb) May be associated with other autoimmune diseases Postablative Hypothyroidism Common cause of thyroid failure in the adult Follows total thyroidectomy secondary to thyroid cancer or subtotal thyroidectomy for Graves’ disease Following treatment with radioactive iodine Athyreotic Hypothyroidism Development defects of the thyroid Incidence 1 in every 4000 newborns Defects – complete absence – failure of thyroid to descend properly during embryologic development Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Most common cause of goitrous hypothyroidism in iodine sufficient areas Autoimmune Endemic Goiter Environmental iodine deficiency Affects more than 200 million people throughout the world Most common in mountainous areas - Alps, Himalayas, and Andes Consumption of cassava meal may aggravate Antithyroid Agents Lithium Para-aminosalicylic acid Phenylbutazone Topically applied resorcinol ethionamide Soybean in infant formulas Iodine-induced Chronic administration of large doses of iodine – may be seen when potassium iodide, radiographic contrast medium, or amiodarone May occur in newborns when women given large quantities of iodine during pregnancy Central Hypothyroidism Due to hypothalamic or pituitary disease May be associated with other pituitary hormone deficiencies May precipitate adrenal crises if thyroid hormone is replaced before hydrocortisone Clinical Features Symptom % Cases Weakness 99 Dry skin 97% Coarse skin 97% Lethargy 91% Slow speech 90% Clinical Features Symptom % Cases Edema of eyelids 90 Sensation of cold 89 Decreased sweating 89 Cold skin 83 Thick tongue 82 Clinical Features Symptom % Cases Facial Edema 79 Coarseness of hair 76 Pallor of skin 67 Memory impairment 66 Constipation 61 Clinical Features Symptom % Cases Weight gain 59 Hair loss 57 Pallor of lips 57 Dyspnea 55 Hoarseness 52 Cardiovascular Cardiac output is decreased Peripheral vascular resistance is increased Blood volume is reduced Elevated cholesterol Increased blood pressure Cardiomegaly Bradycardia Alimentary System Modest weight gain Decreased appetite Constipation Nervous System Essential for development of central nervous system in fetus and newborns Slowing of intellectual functions Psychiatric disorders Myxedema coma Hearing loss “hung-up reflexes” Muscular/Skeletal System Muscle aches and stiffness Increased muscle mass Growth failure in children Delayed maturation of bone Fluids/Electrolytes Decreased renal blood flow Delay in water excretion Hyponatremia Hematopoietic System Normocytic normochromic anemia High incidence of pernicious anemia associated with hypothyroidism Reproductive Function Sexual immaturity Delayed or precocious puberty Galactorrhea Diminished libido menorrhagia Laboratory Free T4 TSH Thyroid antibodies – Thyroid peroxidase antibodies (microsomal antibodies) – Thyroglobulin antibodies Radioactive T3 T4 TBG Resin Euthyroid T4 TBG Resin Hypothyroid T4 T3RU TSH TBG Resin TBG Deficiency T4 T3RU TSH N TBG Resin Primary Hypothyroidism TSH T4 TPO Diagnosis Increase Decrease + Autoimm. Increase Decrease - Postsurg./ irradiation TBG Deficiency T4 T3RU TSH Dec. Inc. N Treatment Oral L-thyroxine therapy – 5-10 ug/kg in newborns – 1-2 ug/kg in adults