* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Biohazards: Risk Management - Bio-Link
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
History of biological warfare wikipedia , lookup
Biological warfare wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
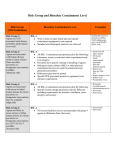
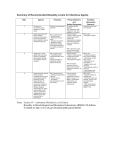
Introduction to Biohazards: Risk Management http://0.tqn.com/d/chemistry/1/0/I/d/biohazard.j pg Biohazards Biological agents with the potential to produce harmful effects in humans H1N1 flu virus http://scienceinthetriangle.org/wpcontent/uploads/2011/01/H1N1-flu-virus.jpg Pathogenicity • The relative ability of an organism to cause disease in humans or other organisms • A pathogenic agent must also be infectious – Those organisms that invade and cause a SPECIFIC host disease are called etiological agents Vibrio cholerae http://remf.dartmouth.edu/imagesindex.html Carriers • An agent infects a host but does not cause disease in that host http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Mallon-Mary_01.jpg Routes of infection • • • • Inhalation Skin/eye contact Ingestion Injection Mold spores http://science.nationalgeographic.com/staticfiles/NGS/Shared/St aticFiles/Science/Images/Content/mold-78761240-sw.jpg Special considerations when working with biohazards • Pathogenic • Associated risks • Laboratoryacquired infections • Treatments • Allergies Hepatitis C virus http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:HCV_EM_picture_2.png Biohazard considerations (con.) • Infectiousness • Limiting exposure • Special safety precautions • Is the level of risk of working with this agent acceptable to the worker? Polio virus http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Polio_EM_PHIL_1875_lores.PNG Laboratory-Acquired Infections (LAI) • Infections that can be traced directly to lab organisms handled by or used in the vicinity of the infected individuals – Thousands documented – Hundreds of deaths Biosafety Guidelines • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.bioethicsinstitute.org/data /images/cdc-785103.jpg • National Institutes of Health (NIH) • Others https://dcb.cit.nih.gov/images/NIH_Logo.gif Standard Microbiological Practices Practices to be used when working with ALL microbiological organisms • Protect worker • Protect culture http://www.asepticsolutions.com/images/streak_plate.JPG Standard Rules for Working with Microbes • Only trained individuals may enter lab • Always wear lab coats and safety glasses • Wash hands after working with organisms and before leaving lab • No eating, drinking, smoking • Avoid hand to mouth or eye contact • No mouth pipetting • Minimize aerosol production • Work on clean hard benchtop and ALWAYS keep disinfectant handy • Decontaminate workspace and waste before disposing Types of Containment Control of biohazards by isolation and separation of organism from worker • Primary containment – Personal containment – Physical containment • Seconary containment – Personal containment – Physical containment http://www.terrauniversal.com/gallery/hoods/Images/biological_s afety_cabinet_purifier_Cover.jpg Biosafety Levels: BSL-1 Well characterized strains not causing disease in healthy humans • Standard Microbiological Practices http://www.lbl.gov/ehs/biosafety/manual/assets/img/4.0_image00 8.jpg Biosafety Levels: BSL-2 Agents may cause disease • Usually treatable or preventable • Need autoclave, special disposal requirements • If aerosols produced, need biological safety cabinet (Class 1 or II) http://engineering.colorado.edu/dlc/laboratories/photos/publicheal th.jpg Biosafety Levels: BSL-3 Severe or lethal human disease • Blood testing for workers • Entry to lab controlled • Physical containment for all manipulations. Extra protective gear (respirators) http://www.dpr.com/images/projects/large/Emory%20BSL3%20L ab%20View%20%232%20-%20large.jpg • No air recirculation, negative airflow Biosafety Levels: BSL4 High risk of lethality, airborne or unknown agent • Clothing change, and shower upon exit • All work done in Class III BSC or Class I or II with full body, air – supplied suit • Must be done in separate building or zone with own contained air system http://www.cdc.gov/media/subtopic/library/LabsScientists/6638S.j pg Biological Safety Cabinets Provides containment for aerosols and separates work area from operator and lab while providing clean air • Able to filter most particles (including most viruses) from air • Does not remove chemical vapors Classes of BSC’s • Class I and Class II cabinets draw air from room and work something like fume hoods http://ehs.virginia.edu/biosafety/bio.images/bsc.jpg • Class III are glove boxes http://eu.escoglobal.com/products/images/products-big/AC3B.jpg