* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.3 powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
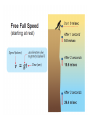
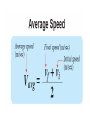
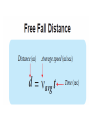
2.3 • Define: • Free Fall-the acceleration of a falling object under the sole influence of Earth’s gravitational force. • Example: Ball thrown upward after the point at which it leaves your hand. • What is not an example of free fall? Birds, helicopters, airplanes • Objects in free fall on Earth accelerate downward at 9.8 2 m/sec . This is called the acceleration due to gravity. The letter g is used to represent its value. • To calculate an object’s speed, you multiply the time it falls by the value of g . Describe what happens when you throw a ball upward in terms of acceleration. (At least 3 sentences) • The ball will decelerate (slow down) as it moves upward at a 2 rate of 9.8m/sec . It will come to a stop for an instant. Then the ball will accelerate (speed up) downward at a rate of 9.8m/sec2. • Define. • Velocity: Speed with direction. • Define. • Weight: force of gravity on an object. • The symbol Fg stands for “force of gravity” and is used to represent weight. Why can’t we use the terms weight and mass interchangeably? • Weight deals with the pull of gravity on an object. Mass simply deals with how much matter something has. • Weight is a force measured in Newtons or pounds. • Define. • Air resistance: The opposing force on a moving object due to the resistance of air. • Example: Feather accelerates at a rate much less than 9.8m/sec2, because of the friction of air. The net force is the weight minus the force of the air pushing up on the feather as it falls. Why does a baseball fall faster than a feather? (at least 3 sentences) • Shape • Force of air resistance much smaller relative to the ball’s weight. • Net force is almost equal to the ball’s weight, so it falls at nearly 9.8 m/sec2 downward. • Define. • Terminal Speed: The maximum speed reached by an object in free fall; the speed at which the force of gravity and air resistance are equal. Why does a crumpled ball of paper have a faster terminal speed than a flat piece of paper? • The flat sheet has more air resistance even though the paper’s weight is the same.