* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2: Exercise Physiology
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
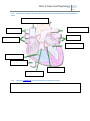
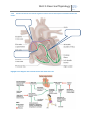
Unit 2: Exercise Physiology Unit 2.1 Key learning intention (KLI) Success criteria Resources Key words Structure and function of the circulatory system Understand how the circulatory system functions and how it is affected by exercise and training. To predict what changes would occur in the cardiovascular system of a trained aerobic athlete. Pages 30-49 Plasma, leucocytes, erythrocytes, thrombocytes READ THE ALL THE RELEVANT RESOURCE PAGES IN YOUR BOOK BEFORE STARTING 2.2.1 State the composition of blood 2.2.2 Distinguish between the functions erythrocytes, leucocytes and platelets Function Erythrocytes Leucocytes Platelets ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 2: Exercise Physiology ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ 2.2.3 Describe the anatomy of the heart with reference to the heart chambers, valves and major blood vessels 2.2.5 Outline the relationship between pulmonary and systemic circulation Unit 2: Exercise Physiology ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ 2.2.4 Describe the intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of heart rate and the sequence of excitation of the heart muscle. Highlight in this diagram other extrinsic factors that affect heart rate Unit 2: Exercise Physiology 2.2.6 Describe the relationship between Cardiac output, stroke volume and heart rate 2.2.7 Analyse CO, SV and HR for different populations during exercise and at rest FEMALE 20 years old Untrained At rest During max exercise 2.2.9 Systolic MALE 60 years old Untrained trained Heart rate (HR) Stroke volume (SV) Cardiac output (Litres) Heart rate Stroke volume Cardiac output Define the terms systolic and diastolic blood pressure Function Diastolic trained ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ 20 years old Untrained 70 trained 22 35 60 years old Untrained trained Unit 2: Exercise Physiology 2.2.10 ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Analyse systolic and diastolic blood pressure data at rest and during exercise Analysis Rhythmic exercise Resistance (static) Upper body Recovery 2.2.11. Discuss how systolic and diastolic blood pressure respond to dynamic and static exercise. Unit 2: Exercise Physiology 2.2.8 2.2.12 Explain cardiovascular drift Compare the distribution of blood at rest and during exercise ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 2: Exercise Physiology Compare the values. Ensure you compare relative and absolute values. 2.2.13 Describe the cardiovascular adaptations resulting from aerobic training Adaptation Blood Heart Blood vessels Muscle ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 2: Exercise Physiology ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ 2.2.14 Explain maximal oxygen consumption (VO2 MAX) 2.2.15. Discuss the variability of maximal oxygen consumption (VO2 Max) in selected groups. VO2 Max Value (ml/kg/min) Trained Untrained male Female Young Old 2.2.16. exercise Discuss the variability of maximal oxygen consumption (VO2 Max) with different modes of